Yeast nuclear envelope subdomains with distinct abilities to resist membrane expansion
- PMID: 16467382
- PMCID: PMC1415286
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-09-0839
Yeast nuclear envelope subdomains with distinct abilities to resist membrane expansion
Abstract
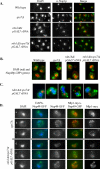
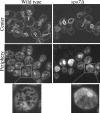
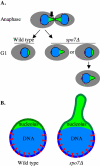
Little is known about what dictates the round shape of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae nucleus. In spo7Delta mutants, the nucleus is misshapen, exhibiting a single protrusion. The Spo7 protein is part of a phosphatase complex that represses phospholipid biosynthesis. Here, we report that the nuclear protrusion of spo7Delta mutants colocalizes with the nucleolus, whereas the nuclear compartment containing the bulk of the DNA is unaffected. Using strains in which the nucleolus is not intimately associated with the nuclear envelope, we show that the single nuclear protrusion of spo7Delta mutants is not a result of nucleolar expansion, but rather a property of the nuclear membrane. We found that in spo7Delta mutants the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane was also expanded. Because the nuclear membrane and the ER are contiguous, this finding indicates that in spo7Delta mutants all ER membranes, with the exception of the membrane surrounding the bulk of the DNA, undergo expansion. Our results suggest that the nuclear envelope has distinct domains that differ in their ability to resist membrane expansion in response to increased phospholipid biosynthesis. We further propose that in budding yeast there is a mechanism, or structure, that restricts nuclear membrane expansion around the bulk of the DNA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vesicle trafficking maintains nuclear shape in Saccharomyces cerevisiae during membrane proliferation.J Cell Biol. 2010 Dec 13;191(6):1079-88. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201006083. Epub 2010 Dec 6. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21135138 Free PMC article.
-
Seipin is involved in the regulation of phosphatidic acid metabolism at a subdomain of the nuclear envelope in yeast.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Nov;1851(11):1450-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26275961
-
The yeast lipin Smp2 couples phospholipid biosynthesis to nuclear membrane growth.EMBO J. 2005 Jun 1;24(11):1931-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600672. Epub 2005 May 5. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 15889145 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic approaches to nuclear pore structure and function.Trends Genet. 1995 Jun;11(6):235-41. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89057-5. Trends Genet. 1995. PMID: 7638906 Review.
-
Degradation-mediated protein quality control at the inner nuclear membrane.Nucleus. 2016;7(1):41-9. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1139273. Nucleus. 2016. PMID: 26760377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Shaping the nucleus: factors and forces.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Sep;113(9):2813-21. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24178. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22566057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of diverse nuclear shapes: pathways working independently, together.Commun Integr Biol. 2021 Jul 5;14(1):158-175. doi: 10.1080/19420889.2021.1939942. eCollection 2021. Commun Integr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34262635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mitotic nuclear envelope tether for Gle1 also impacts nuclear and nucleolar architecture.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Sep 14;27(23):3757-70. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-07-0544. Online ahead of print. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27630260 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the Role of the Yeast Lysine Acetyltransferase NuA4 in the Regulation of Nuclear Shape and Lipid Metabolism.Mol Cell Biol. 2024;44(7):273-288. doi: 10.1080/10985549.2024.2366206. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38961766 Free PMC article.
-
Divergence of mitotic strategies in fission yeasts.Nucleus. 2012 May-Jun;3(3):220-5. doi: 10.4161/nucl.19514. Epub 2012 May 1. Nucleus. 2012. PMID: 22572960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fabre, E., and Hurt, E. (1997). Yeast genetics to dissect the nuclear pore complex and nucleocytoplasmic trafficking. Annu. Rev. Genet. 31, 277–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

