cdc2/cyclin B1-dependent phosphorylation of EBNA2 at Ser243 regulates its function in mitosis
- PMID: 16439560
- PMCID: PMC1367142
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.80.4.2045-2050.2006
cdc2/cyclin B1-dependent phosphorylation of EBNA2 at Ser243 regulates its function in mitosis
Abstract
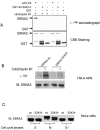
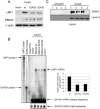
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) transactivates EBV genes in latently infected B cells. We have shown that mitotic hyperphosphorylation of EBNA2 suppresses its ability to transactivate the latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) promoter. In this follow-up study, we identify EBNA2 Ser243 as a phosphorylation site for mitotic cdc2/cyclin B1 kinase. Mutation at Ser243, which mimics constitutive phosphorylation of the protein, decreases endogenous levels of both LMP1 and EBNA2. Moreover, mutation at Ser243 reduces the ability of EBNA2 to transactivate Cp, the promoter for all six EBV EBNA genes. Our data implicate EBNA2 Ser243 as a cdc2/cyclin B1 site of phosphorylation important for EBNA2's cotranscriptional function in mitosis.
Figures
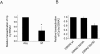


Similar articles
-
Mitosis-specific hyperphosphorylation of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 suppresses its function.J Virol. 2004 Apr;78(7):3542-52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.7.3542-3552.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15016877 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperphosphorylation of EBNA2 by Epstein-Barr virus protein kinase suppresses transactivation of the LMP1 promoter.J Virol. 2005 May;79(9):5880-5. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.9.5880-5885.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15827205 Free PMC article.
-
Domains of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) involved in the transactivation of the latent membrane protein 1 and the EBNA Cp promoters.J Gen Virol. 1995 Nov;76 ( Pt 11):2669-78. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-11-2669. J Gen Virol. 1995. PMID: 7595374
-
[Effect of EB virus latent membrane protein 1 on mitosis control of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE1].Ai Zheng. 2004 May;23(5):512-6. Ai Zheng. 2004. PMID: 15142445 Chinese.
-
PU box-binding transcription factors and a POU domain protein cooperate in the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2-induced transactivation of the EBV latent membrane protein 1 promoter.J Gen Virol. 1995 Nov;76 ( Pt 11):2679-92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-11-2679. J Gen Virol. 1995. PMID: 7595375
Cited by
-
Asymmetric Arginine dimethylation of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 promotes DNA targeting.Virology. 2010 Feb 20;397(2):299-310. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.11.023. Epub 2009 Dec 6. Virology. 2010. PMID: 19969318 Free PMC article.
-
Species-specific functions of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) reveal dual roles for initiation and maintenance of B cell immortalization.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Dec 20;13(12):e1006772. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006772. eCollection 2017 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 29261800 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant cytoplasmic expression of cyclin B1 protein and its correlation with EBV-LMP1, P53 and P16(INK4A) in classical Hodgkin lymphoma in China.Pathol Oncol Res. 2011 Jun;17(2):369-73. doi: 10.1007/s12253-010-9335-x. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Pathol Oncol Res. 2011. PMID: 21174181
-
RNA polymerase II stalling promotes nucleosome occlusion and pTEFb recruitment to drive immortalization by Epstein-Barr virus.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002334. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002334. Epub 2011 Oct 27. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22046134 Free PMC article.
-
PLK1-dependent phosphorylation restrains EBNA2 activity and lymphomagenesis in EBV-infected mice.EMBO Rep. 2021 Dec 6;22(12):e53007. doi: 10.15252/embr.202153007. Epub 2021 Oct 4. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 34605140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberts, B. B. D., J. Lewis, M. Raff, K. Roberts, and J. D. Watson. 1989. Cell growth and division, p.729-790. In R. Adams and A. Walker (ed.), Molecular biology of the cell. Garland Publishing, Inc., New York, N.Y.
-
- Aviel, S., G. Winberg, M. Massucci, and A. Ciechanover. 2000. Degradation of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway: targeting via ubiquitination of the N-terminal residue. J. Biol. Chem. 275:23491-23499. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet, M., J. M. Guinebretiere, E. Kremmer, V. Grunewald, E. Benhamou, G. Contesso, and I. Joab. 1999. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in invasive breast cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 91:1376-1381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

