Assessing the clinical significance of botanical supplementation on human cytochrome P450 3A activity: comparison of a milk thistle and black cohosh product to rifampin and clarithromycin
- PMID: 16432272
- PMCID: PMC1865122
- DOI: 10.1177/0091270005284854
Assessing the clinical significance of botanical supplementation on human cytochrome P450 3A activity: comparison of a milk thistle and black cohosh product to rifampin and clarithromycin
Abstract
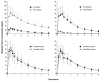
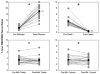
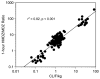
Phytochemical-mediated modulation of cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) may underlie many herb-drug interactions. This study's purpose was to assess the effects of milk thistle and black cohosh supplementation on CYP3A activity and compare them to a clinically recognized inducer, rifampin, and inhibitor, clarithromycin. Healthy volunteers were randomly assigned to receive a standardized milk thistle (900 mg) or black cohosh (80 mg) supplement for 14 days. Subjects also received rifampin (600 mg) and clarithromycin (1000 mg) for 7 days as positive controls for CYP3A induction and inhibition, respectively. Midazolam was administered orally before and after each supplementation and control period. The effects of milk thistle, black cohosh, rifampin, and clarithromycin on midazolam pharmacokinetics were determined using noncompartmental techniques. Unlike those observed for rifampin and clarithromycin, midazolam pharmacokinetics was unaffected by milk thistle or black cohosh. Milk thistle and black cohosh appear to have no clinically relevant effect on CYP3A activity in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of milk thistle (Silybum marianum) and black cohosh (Cimicifuga racemosa) supplementation on digoxin pharmacokinetics in humans.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Jan;34(1):69-74. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.006312. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16221754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
In vivo assessment of botanical supplementation on human cytochrome P450 phenotypes: Citrus aurantium, Echinacea purpurea, milk thistle, and saw palmetto.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Nov;76(5):428-40. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2004.07.007. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15536458 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of age, sex, and rifampin administration on intestinal and hepatic cytochrome P450 3A activity.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Sep;74(3):275-87. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9236(03)00187-5. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12966371 Clinical Trial.
-
Relevance of in vitro and clinical data for predicting CYP3A4-mediated herb-drug interactions in cancer patients.Cancer Treat Rev. 2013 Nov;39(7):773-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.12.008. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013. PMID: 23394826 Review.
-
Rifampin and rifabutin drug interactions: an update.Arch Intern Med. 2002 May 13;162(9):985-92. doi: 10.1001/archinte.162.9.985. Arch Intern Med. 2002. PMID: 11996607 Review.
Cited by
-
Herb-Drug Interaction in Inflammatory Diseases: Review of Phytomedicine and Herbal Supplements.J Clin Med. 2022 Mar 12;11(6):1567. doi: 10.3390/jcm11061567. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35329893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two flavonolignans from milk thistle (Silybum marianum) inhibit CYP2C9-mediated warfarin metabolism at clinically achievable concentrations.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Mar;332(3):1081-7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.161927. Epub 2009 Nov 24. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 19934397 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of milk thistle on the pharmacokinetics of darunavir-ritonavir in HIV-infected patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jun;56(6):2837-41. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00025-12. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22430963 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Strong CYP3A Inhibition and Induction on the Pharmacokinetics of Ixazomib, an Oral Proteasome Inhibitor: Results of Drug-Drug Interaction Studies in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors or Lymphoma and a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Analysis.J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Feb;58(2):180-192. doi: 10.1002/jcph.988. Epub 2017 Aug 11. J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28800141 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
PBPK Models for CYP3A4 and P-gp DDI Prediction: A Modeling Network of Rifampicin, Itraconazole, Clarithromycin, Midazolam, Alfentanil, and Digoxin.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2018 Oct;7(10):647-659. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12343. Epub 2018 Sep 7. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30091221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Committee on the Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine by the American Public. Complementary and Alternative Medicine in the United States. The National Academies Press; Washington, DC: 2005. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Rosenberg L, Anderson TE, Mitchell AA. Recent patterns of medication use in the ambulatory adult population of the United States. JAMA. 2002;287:337–344. - PubMed
-
- Brazier NC, Levine MAH. Drug-herb interactions among commonly used conventional medicines: a compendium for health care professionals. Am J Ther. 2003;10:163–169. - PubMed
-
- Hu Z, Yang X, Ho PCL, Chan SY, Heng PWS, Chan E, Duan W, Kph HL, Zhou S. Herb-drug interactions: a literature review. Drugs. 2005;65:1239–1282. - PubMed
-
- Wentworth JM, Agostini M, Love J, Schwabe JW, Chatterjee VKK. St. John’s wort, a herbal antidepressant, activates the steroid X receptor. J Endocrinol. 2000;166:R11–R16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

