Molecular cloning and characterization of crustacean type-one dopamine receptors: D1alphaPan and D1betaPan
- PMID: 16426885
- PMCID: PMC4019047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2005.11.017
Molecular cloning and characterization of crustacean type-one dopamine receptors: D1alphaPan and D1betaPan
Abstract
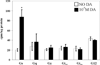
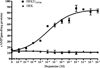
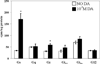
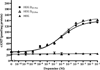
Dopamine (DA) differentially modulates identified neurons in the crustacean stomatogastric nervous system (STNS). While the electrophysiological actions of DA have been well characterized, little is known about the dopaminergic transduction cascades operating in this system. As a first step toward illuminating the molecular underpinnings of dopaminergic signal transduction in the crustacean STNS, we have cloned and characterized two type-one DA receptors (DARs) from the spiny lobster (Panulirus interruptus): D(1alphaPan) and D(1betaPan). We found that the structure and function of these arthropod DARs are well conserved across species. Using a heterologous expression system, we determined that DA, but not serotonin, octopamine, tyramine or histamine activates these receptors. When stably expressed in HEK cells, the D(1alphaPan) receptor couples with Gs, and DA elicits an increase in [cAMP]. The D(1betaPan) receptor responds to DA with a net increase in [cAMP] that is mediated by Gs and Gz.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Arthropod D2 receptors positively couple with cAMP through the Gi/o protein family.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Jan;146(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2006.08.018. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17134931 Free PMC article.
-
Crustacean dopamine receptors: localization and G protein coupling in the stomatogastric ganglion.J Neurochem. 2008 Feb;104(4):1006-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05029.x. Epub 2007 Nov 6. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 17986222 Free PMC article.
-
Cell specific dopamine modulation of the transient potassium current in the pyloric network by the canonical D1 receptor signal transduction cascade.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Aug;104(2):873-84. doi: 10.1152/jn.00195.2010. Epub 2010 Jun 2. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20519576 Free PMC article.
-
Arthropod 5-HT2 receptors: a neurohormonal receptor in decapod crustaceans that displays agonist independent activity resulting from an evolutionary alteration to the DRY motif.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 31;24(13):3421-35. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0062-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15056722 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of cloned human dopamine D1 receptor-mediated calcium release in 293 cells.Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;47(1):131-9. Mol Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 7838121
Cited by
-
Neuromodulation of neuronal circuits: back to the future.Neuron. 2012 Oct 4;76(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.010. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23040802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of putative amine receptor complement in the eyestalk of the crayfish, Procambarus clarkii.Invert Neurosci. 2019 Sep 23;19(4):12. doi: 10.1007/s10158-019-0232-z. Invert Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31549228
-
Arthropod D2 receptors positively couple with cAMP through the Gi/o protein family.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Jan;146(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2006.08.018. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17134931 Free PMC article.
-
Honey bee dopamine and octopamine receptors linked to intracellular calcium signaling have a close phylogenetic and pharmacological relationship.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e26809. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026809. Epub 2011 Nov 11. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22096499 Free PMC article.
-
Two dopamine D2-like receptor genes from the silkworm (Bombyx mori) and their evolutionary history in metazoan.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 28;7(1):6848. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07055-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28754962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banihashemi B, Albert PR. Dopamine-D2S receptor inhibition of calcium influx, adenylyl cyclase, and mitogen-activated protein kinase in pituitary cells: distinct Galpha and Gbetagamma requirements. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002;16:2393–2404. - PubMed
-
- Beltz BS. Distribution and functional anatomy of amine-containing neurons in decapod crustaceans. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1999;44:105–120. - PubMed
-
- Blenau W, Erber J, Baumann A. Characterization of a dopamine D1 receptor from Apis mellifera: cloning, functional expression, pharmacology, and mRNA localization in the brain. J. Neurochem. 1998;70:15–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

