Fetomaternal cross talk in the placental vascular bed: control of coagulation by trophoblast cells
- PMID: 16380449
- PMCID: PMC1895751
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-10-4111
Fetomaternal cross talk in the placental vascular bed: control of coagulation by trophoblast cells
Abstract
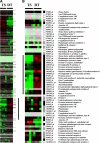
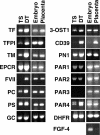
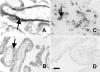
Humans and rodents exhibit a peculiar type of placentation in which zygote-derived trophoblast cells, rather than endothelial cells, line the terminal maternal vascular space. This peculiar aspect of the placental vasculature raises important questions about the relative contribution of fetal and maternal factors in the local control of hemostasis in the placenta and how these might determine the phenotypic expression of thrombophilia-associated complications of pregnancy. Using genomewide expression analysis, we identify a panel of genes that determine the ability of fetal trophoblast cells to regulate hemostasis at the fetomaternal interface. We show that spontaneous differentiation of trophoblast stem cells is associated with the acquisition of an endothelial cell-like thromboregulatory gene expression program. This program is developmentally regulated and conserved between mice and humans. We further show that trophoblast cells sense, via the expression of protease activated receptors, the presence of activated coagulation factors. Engagement of these receptors results in cell-type specific changes in gene expression. Our observations define candidate fetal genes that are potential risk modifiers of maternal thrombophilia-associated pregnancy complications and provide evidence that coagulation activation at the fetomaternal interface can affect trophoblast physiology altering placental function in the absence of frank thrombosis.
Figures

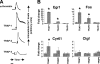
Similar articles
-
Atypical protein kinase C iota (PKCλ/ι) ensures mammalian development by establishing the maternal-fetal exchange interface.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jun 23;117(25):14280-14291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1920201117. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32513715 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between trophoblast cells and the maternal and fetal circulation in the mouse placenta.Dev Biol. 2002 Oct 15;250(2):358-73. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(02)90773-6. Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 12376109
-
Intersection of regulatory pathways controlling hemostasis and hemochorial placentation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Dec 14;118(50):e2111267118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2111267118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34876522 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell insights into human trophoblast lineage differentiation.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Dec;23(1):77-103. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw026. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 27591247 Review.
-
How to make a placenta: mechanisms of trophoblast cell differentiation in mice--a review.Placenta. 2005 Apr;26 Suppl A:S3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2005.01.015. Placenta. 2005. PMID: 15837063 Review.
Cited by
-
X chromosome-dependent disruption of placental regulatory networks in hybrid dwarf hamsters.Genetics. 2021 May 17;218(1):iyab043. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab043. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33710276 Free PMC article.
-
The endothelial protein C receptor plays an essential role in the maintenance of pregnancy.Sci Adv. 2020 Nov 6;6(45):eabb6196. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb6196. Print 2020 Nov. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 33158859 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Par4 and platelets contribute to defective placenta formation in mouse embryos lacking thrombomodulin.Blood. 2008 Aug 1;112(3):585-91. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-111302. Epub 2008 May 19. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18490515 Free PMC article.
-
Maintaining extraembryonic expression allows generation of mice with severe tissue factor pathway inhibitor deficiency.Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 12;3(3):489-498. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018018853. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 30755437 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous tissue factor pathway inhibitor in vascular smooth muscle cells inhibits arterial thrombosis.Front Med. 2017 Sep;11(3):403-409. doi: 10.1007/s11684-017-0522-y. Epub 2017 May 27. Front Med. 2017. PMID: 28550640
References
-
- Adamson SL, Lu Y, Whiteley KJ, et al. Interactions between trophoblast cells and the maternal and fetal circulation in the mouse placenta. Dev Biol. 2002;250: 358-373. - PubMed
-
- Georgiades P, Ferguson-Smith AC, Burton GJ. Comparative developmental anatomy of the murine and human definitive placentae. Placenta. 2002;23: 3-19. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka S, Kunath T, Hadjantonakis AK, Nagy A, Rossant J. Promotion of trophoblast stem cell proliferation by FGF4. Science. 1998;282: 2072-2075. - PubMed
-
- Weiler-Guettler H, Aird WC, Rayburn H, Husain M, Rosenberg RD. Developmentally regulated gene expression of thrombomodulin in postimplantation mouse embryos. Development. 1996;122: 2271-2281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

