Programmed death-1 (PD-1):PD-ligand 1 interactions inhibit TCR-mediated positive selection of thymocytes
- PMID: 16301644
- PMCID: PMC2779139
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.11.7372
Programmed death-1 (PD-1):PD-ligand 1 interactions inhibit TCR-mediated positive selection of thymocytes
Abstract
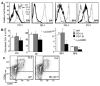
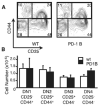
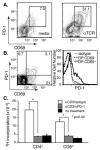
Positive selection during thymocyte development is driven by the affinity and avidity of the TCR for MHC-peptide complexes expressed in the thymus. In this study, we show that programmed death-1 (PD-1), a member of the B7/CD28 family of costimulatory receptors, inhibits TCR-mediated positive selection through PD-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1):PD-1 interactions. Transgenic mice that constitutively overexpress PD-1 on CD4+CD8+ thymocytes display defects in positive selection in vivo. Using an in vitro model system, we find that PD-1 is up-regulated following TCR engagement on CD4+CD8+ murine thymocytes. Coligation of TCR and PD-1 on CD4+CD8+ thymocytes with a novel PD-1 agonistic mAb inhibits the activation of ERK and up-regulation of bcl-2, both of which are downstream mediators essential for positive selection. Inhibitory signals through PD-1 can overcome the ability of positive costimulators, such as CD2 and CD28, to facilitate positive selection. Finally, defects in positive selection that result from PD-1 overexpression in thymocytes resolve upon elimination of PD-L1, but not PD-1 ligand 2, expression. PD-L1-deficient mice have increased numbers of CD4+CD8+ and CD4+ thymocytes, indicating that PD-L1 is involved in normal thymic selection. These data demonstrate that PD-1:PD-L1 interactions are critical to positive selection and play a role in shaping the T cell repertoire.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

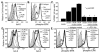
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the role of negative T cell costimulatory pathways in CD4 and CD8 T cell-mediated alloimmune responses in vivo.J Immunol. 2005 Jun 1;174(11):6648-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.11.6648. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15905503
-
Maturation versus death of developing double-positive thymocytes reflects competing effects on Bcl-2 expression and can be regulated by the intensity of CD28 costimulation.J Immunol. 2001 Mar 1;166(5):3468-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.5.3468. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11207305
-
Clonal deletion and the fate of autoreactive thymocytes that survive negative selection.Nat Immunol. 2012 Apr 29;13(6):569-78. doi: 10.1038/ni.2292. Nat Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22544394 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between the T cell antigen receptor and the glucocorticoid receptor regulates thymocyte development.Stem Cells. 1996 Sep;14(5):490-500. doi: 10.1002/stem.140490. Stem Cells. 1996. PMID: 8888490 Review.
-
Negative regulation of T-cell function by PD-1.Crit Rev Immunol. 2004;24(4):229-37. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v24.i4.10. Crit Rev Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15588223 Review.
Cited by
-
Strength of PD-1 signaling differentially affects T-cell effector functions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 2;110(27):E2480-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305394110. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23610399 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analyses of Genes Associated with Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes.J Immunol Res. 2020 Oct 6;2020:1025857. doi: 10.1155/2020/1025857. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 33083497 Free PMC article.
-
Agonist redirected checkpoint, PD1-Fc-OX40L, for cancer immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Dec 18;6(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0454-3. J Immunother Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30563566 Free PMC article.
-
CD55 Is Essential for CD103+ Dendritic Cell Tolerogenic Responses that Protect against Autoimmunity.Am J Pathol. 2019 Jul;189(7):1386-1401. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.04.008. Epub 2019 May 17. Am J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31103439 Free PMC article.
-
The diversity of costimulatory and inhibitory receptor pathways and the regulation of antiviral T cell responses.Curr Opin Immunol. 2009 Apr;21(2):179-86. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2009.01.010. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19264470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Starr TK, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Positive and negative selection of T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:139–176. - PubMed
-
- Greenwald RJ, Latchman YE, Sharpe AH. Negative co-receptors on lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:391–396. - PubMed
-
- Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary D, Borde M, Chernova I, Iwai Y, Long AJ, Brown JA, Nunes R, et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:261–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

