Species- and cell type-specific interactions between CD47 and human SIRPalpha
- PMID: 16291597
- PMCID: PMC1895743
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-04-1463
Species- and cell type-specific interactions between CD47 and human SIRPalpha
Abstract
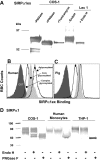
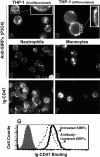
CD47 on red blood cells (RBCs) reportedly signals "self" by binding SIRPalpha on phagocytes, at least in mice. Such interactions across and within species, from mouse to human, are not yet clear and neither is the relation to cell adhesion. Using human SIRPalpha1 as a probe, antibody-inhibitable binding to CD47 was found only with human and pig RBCs (not mouse, rat, or cow). In addition, CD47-mediated adhesion of human and pig RBCs to SIRPalpha1 surfaces resists sustained forces in centrifugation (as confirmed by atomic force microscopy) but only at SIRPalpha-coating densities far above those measurable on human neutrophils, monocytes, and THP-1 macrophages. While interactions strengthen with deglycosylation of SIRPalpha1, low copy numbers explain the absence of RBC adhesion to phagocytes under physiologic conditions and imply that the interaction being studied is not responsible for red cell clearance in humans. Evidence of clustering nonetheless suggests mechanisms of avidity enhancement. Finally, using the same CD47 antibodies and soluble SIRPalpha1, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells were assayed and found to display CD47 but not bind SIRPalpha1 significantly. The results thus demonstrate that SIRPalpha-CD47 interactions, which reportedly define self, exhibit cell type specificity and limited cross-species reactivity.
Figures
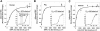
Similar articles
-
Phylogenetic divergence of CD47 interactions with human signal regulatory protein alpha reveals locus of species specificity. Implications for the binding site.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jan 19;282(3):1805-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603923200. Epub 2006 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17098740
-
'Clustering' SIRPα into the plasma membrane lipid microdomains is required for activated monocytes and macrophages to mediate effective cell surface interactions with CD47.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 15;8(10):e77615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077615. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24143245 Free PMC article.
-
Functional CD47/signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRP(alpha)) interaction is required for optimal human T- and natural killer- (NK) cell homeostasis in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 9;108(32):13224-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1101398108. Epub 2011 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21788504 Free PMC article.
-
The CD47-SIRPα signaling axis as an innate immune checkpoint in cancer.Immunol Rev. 2017 Mar;276(1):145-164. doi: 10.1111/imr.12527. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28258703 Review.
-
CD47/SIRPα pathway mediates cancer immune escape and immunotherapy.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jul 25;17(13):3281-3287. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.60782. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34512146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Addressing the Inflammatory Response to Clinically Relevant Polymers by Manipulating the Host Response Using ITIM Domain-Containing Receptors.Polymers (Basel). 2014 Sep 29;6(10):2526-2551. doi: 10.3390/polym6102526. Polymers (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25705515 Free PMC article.
-
A pH-dependent anti-CD47 antibody that selectively targets solid tumors and improves therapeutic efficacy and safety.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jan 17;16(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01399-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36650558 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressing or Enhancing Macrophage Engulfment through the Use of CD47 and Related Peptides.Bioconjug Chem. 2022 Nov 16;33(11):1989-1995. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00019. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Bioconjug Chem. 2022. PMID: 35316023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic modification of adeno-associated viral vector type 2 capsid enhances gene transfer efficiency in polarized human airway epithelial cells.Hum Gene Ther. 2008 Dec;19(12):1407-14. doi: 10.1089/hum.2008.117. Hum Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 18778196 Free PMC article.
-
CD20-selective inhibition of CD47-SIRPα "don't eat me" signaling with a bispecific antibody-derivative enhances the anticancer activity of daratumumab, alemtuzumab and obinutuzumab.Oncoimmunology. 2017 Oct 31;7(2):e1386361. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1386361. eCollection 2018. Oncoimmunology. 2017. PMID: 29308308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Y, Buhring HJ, Zen K, et al. Signal regulatory protein (SIRPalpha), a cellular ligand for CD47, regulates neutrophil transmigration. J Biol Chem. 2002;277: 10028-10036. - PubMed
-
- Latour S, Tanaka H, Demeure C, et al. Bidirectional negative regulation of human T and dendritic cells by CD47 and its cognate receptor signal-regulator protein-alpha: down-regulation of IL-12 responsiveness and inhibition of dendritic cell activation. J Immunol. 2001;167: 2547-2554. - PubMed
-
- Seiffert M, Brossart P, Cant C, et al. Signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPalpha) but not SIRPbeta is involved in T-cell activation, binds to CD47 with high affinity, and is expressed on immature CD34(+)CD38(-) hematopoietic cells. Blood. 2001;97: 2741-2749. - PubMed
-
- Oldenborg PA, Zheleznyak A, Fang YF, Lagenaur CF, Gresham HD, Lindberg FP. Role of CD47 as a marker of self on red blood cells. Science. 2000;288: 2051-2054. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

