Systematic evaluation and comparison of statistical tests for publication bias
- PMID: 16276033
- PMCID: PMC7904376
- DOI: 10.2188/jea.15.235
Systematic evaluation and comparison of statistical tests for publication bias
Abstract
Background: This study evaluates the statistical and discriminatory powers of three statistical test methods (Begg's, Egger's, and Macaskill's) to detect publication bias in meta-analyses.
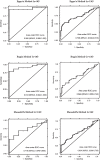
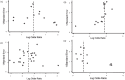
Methods: The data sources were 130 reviews from the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2002 issue, which considered a binary endpoint and contained 10 or more individual studies. Funnel plots with observers'agreements were selected as a reference standard. We evaluated a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity by varying cut-off p-values, power of statistical tests given fixed false positive rates, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.
Results: In 36 reviews, 733 original studies evaluated 2,874,006 subjects. The number of trials included in each ranged from 10 to 70 (median 14.5). Given that the false positive rate was 0.1, the sensitivity of Egger's method was 0.93, and was larger than that of Begg's method (0.86) and Macaskill's method (0.43). The sensitivities of three statistical tests increased as the cut-off p-values increased without a substantial decrement of specificities. The area under the ROC curve of Egger's method was 0.955 (95% confidence interval, 0.889-1.000) and was not different from that of Begg's method (area=0.913, p=0.2302), but it was larger than that of Macaskill's method (area=0.719, p=0.0116).
Conclusion: Egger's linear regression method and Begg's method had stronger statistical and discriminatory powers than Macaskill's method for detecting publication bias given the same type I error level. The power of these methods could be improved by increasing the cut-off p-value without a substantial increment of false positive rate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Empirical Comparison of Publication Bias Tests in Meta-Analysis.J Gen Intern Med. 2018 Aug;33(8):1260-1267. doi: 10.1007/s11606-018-4425-7. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Gen Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29663281 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias in meta-analysis.JAMA. 2006 Feb 8;295(6):676-80. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.6.676. JAMA. 2006. PMID: 16467236
-
Investigation of publication bias in meta-analyses of diagnostic test accuracy: a meta-epidemiological study.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014 May 23;14:70. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-14-70. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014. PMID: 24884381 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical controversies in clinical research: publication bias evaluations are not routinely conducted in clinical oncology systematic reviews.Ann Oncol. 2017 May 1;28(5):931-937. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw691. Ann Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28039176 Review.
-
Publication bias in meta-analyses of the efficacy of psychotherapeutic interventions for schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2012 Jul;138(2-3):103-12. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2012.03.023. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Schizophr Res. 2012. PMID: 22484024 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of glucose-lowering drugs in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 11;13:897776. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.897776. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36034458 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Infection Increases the Risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Meta-Analysis.Chest. 2020 May;157(5):1175-1187. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.10.032. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Chest. 2020. PMID: 31730835 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21 gene rs6822844 polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jan 31;40(1):BSR20191449. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191449. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31763680 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Face-to-Face and eHealth Blended Interventions on Physical Activity, Diet, and Weight-Related Outcomes among Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 14;20(2):1560. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20021560. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36674317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An updated association between TNF-α -238G/A polymorphism and gastric cancer susceptibility in East Asians.Biosci Rep. 2018 Dec 14;38(6):BSR20181231. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181231. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30413607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Easterbrook PJ, Berlin JA, Gopalan R, Matthews DR. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet 1991; 337: 867-72. - PubMed
-
- De Angelis C, Drazen JM, Frizelle FA, Haug C, Hoey J, Horton R, et al. . Clinical trial registration: a statement from the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1250-1. - PubMed
-
- Greenland S Invited commentary: a critical look at some popular meta-analytic methods. Am J Epidemiol 1994; 140: 290-6. - PubMed
-
- Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994; 50: 1088-101. - PubMed

