Expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 and their effects on angiogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 16273602
- PMCID: PMC4436713
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.5931
Expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 and their effects on angiogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To determine the expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and to investigate the relationship between iNOS and MMP-9 expression and their effects on angiogenesis and progression of HCC.
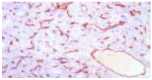
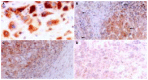
Methods: In this study, we examined iNOS, MMP-9, and CD34 expression in specimens surgically removed from 32 HCC patients and 7 normal liver tissues by immunohistochemical staining. Meanwhile, microvessel density (MVD) was determined as a marker of angiogenesis by counting CD34-positive cells.
Results: The positive rates of iNOS and MMP-9 expression were 71.88% (23/32) and 78.13% (25/32) in HCC. MMP-9 expression was significantly correlated with tumor size, capsule status, TNM stage, and risk of HCC recurrence (P = 0.032, P = 0.033, P = 0.007, and P = 0.001, respectively). There was also a significant relationship between iNOS expression and capsule status and risk of HCC recurrence (P = 0.049 and P = 0.004, respectively), but no correlation between iNOS expression and tumor size and TNM stage. There was a positive association between MVD and TNM stage and risk of HCC recurrence (P = 0.037 and P = 0.000, respectively). The count of MVD was significantly different in different iNOS and MMP-9 immunoreactivity groups (F = 17.713 and 17.097, P = 0.000 and P = 0.000, respectively). The examination of Spearman's rank correlation coefficient showed that there was a significant positive correlation between MVD and iNOS, MMP-9 immunoreactivity (r = 0.754 and 0.751, P = 0.000 and P=0.000, respectively). There was also a significant association between MMP-9 and iNOS expression in HCC (P = 0.010).
Conclusion: Nitric oxide (NO) produced by iNOS could modulate MMP-9 production and therefore contribute to tumor cell angiogenesis and invasion and metastasis in HCC. The strong expression of iNOS and MMP-9 in HCC may be helpful in evaluating the recurrence of HCC, predicting poor prognosis. For patients with strong expression of MMP-9 and iNOS, the optimal treatment scheme needs to be selected.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and vascular endothelial growth factor and their relationship with microvessel density in hepatocellular carcinoma].Ai Zheng. 2005 Jan;24(1):99-103. Ai Zheng. 2005. PMID: 15642211 Chinese.
-
Relationship between the expression of iNOS,VEGF,tumor angiogenesis and gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Aug;8(4):591-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i4.591. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 12174362 Free PMC article.
-
[Nitric oxide synthase and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and their relation to angiogenesis].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2000 Jul;22(4):301-3. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2000. PMID: 11778555 Chinese.
-
Unveiling the significance of inducible nitric oxide synthase: Its impact on cancer progression and clinical implications.Cancer Lett. 2024 Jun 28;592:216931. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216931. Epub 2024 May 1. Cancer Lett. 2024. PMID: 38701892 Review.
-
Evaluation of Intra-Tumoral Vascularization in Hepatocellular Carcinomas.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Oct 27;7:584250. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.584250. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33195338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in the Carcinogenesis of Gastrointestinal Cancers.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017 Jun 20;26(18):1059-1077. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6850. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017. PMID: 27494631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A correlative study between IVIM-DWI parameters and VEGF and MMPs expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Mar 1;13(3):1887-1898. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-271. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 36915336 Free PMC article.
-
A new procedure for determining the genetic basis of a physiological process in a non-model species, illustrated by cold induced angiogenesis in the carp.BMC Genomics. 2009 Oct 23;10:490. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-490. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19852815 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric Oxide (NO) and NO Synthases (NOS)-Based Targeted Therapy for Colon Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 13;12(7):1881. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071881. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32668616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Value of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) in Human Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jun 4;2019:6304851. doi: 10.1155/2019/6304851. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31275981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Folkman J. What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990;82:4–6. - PubMed
-
- Stetler-Stevenson WG, Liotta LA, Kleiner DE. Extracellular matrix 6: role of matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion and metastasis. FASEB J. 1993;7:1434–1441. - PubMed
-
- Westermarck J, Kähäri VM. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in tumor invasion. FASEB J. 1999;13:781–792. - PubMed
-
- Curran S, Murray GI. Matrix metalloproteinases: molecular aspects of their roles in tumour invasion and metastasis. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36:1621–1630. - PubMed
-
- Yoshizaki T, Sato H, Furukawa M. Recent advances in the regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 2 activation: from basic research to clinical implication (Review) Oncol Rep. 2002;9:607–611. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

