TaqMan real-time reverse transcription-PCR and JDVp26 antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to quantify Jembrana disease virus load during the acute phase of in vivo infection
- PMID: 16272489
- PMCID: PMC1287780
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.11.5574-5580.2005
TaqMan real-time reverse transcription-PCR and JDVp26 antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to quantify Jembrana disease virus load during the acute phase of in vivo infection
Erratum in
- J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Jun;45(6):2100
Abstract
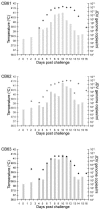
Jembrana disease virus (JDV) is an acutely pathogenic lentivirus that affects Bali cattle in Indonesia. The inability to propagate the virus in vitro has made it difficult to quantitate JDV and determine the kinetics of virus replication during the acute phase of the disease process. We report for the first time two techniques that enable quantification of the virus and the use of these techniques to quantify the virus load during the acute phase of the disease process. A one-step JDV gag [corrected] TaqMan real-time reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) assay was developed for the detection and quantification of JDV RNA in plasma. The limit of detection was 9.8 x 10(2) JDV viral RNA copies over 35 cycles, equivalent to 4.2 x 10(4) JDV genome copies/ml, and a peak virus load of 1.6 x 10(12) during the acute febrile period. An antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was also developed to quantify the levels of JDV capsid (JDVp26) over a linear range of 10 to 200 ng/ml. Viral RNA and JDVp26 levels were correlated in 48 plasma samples obtained from experimentally infected cattle. A significant positive correlation (R = 0.860 and r(2) = 0.740) was observed between the two techniques within the range of their detection limits. The relatively insensitive capture ELISA provides an economical and feasible method for monitoring of virus in the absence of more sensitive techniques.
Figures

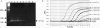
Similar articles
-
Comparison of immunoassay and real-time PCR methods for the detection of Jembrana disease virus infection in Bali cattle.J Virol Methods. 2009 Jul;159(1):81-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.03.005. Epub 2009 Mar 18. J Virol Methods. 2009. PMID: 19442849
-
Analysis of Jembrana disease virus replication dynamics in vivo reveals strain variation and atypical responses to infection.Virology. 2009 Apr 10;386(2):310-6. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.01.014. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19230948
-
Prior bovine immunodeficiency virus infection does not inhibit subsequent superinfection by the acutely pathogenic Jembrana disease virus.Virology. 2010 Sep 1;404(2):261-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.05.001. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Virology. 2010. PMID: 20570311
-
Jembrana disease virus: host responses, viral dynamics and disease control.Curr HIV Res. 2010 Jan;8(1):53-65. doi: 10.2174/157016210790416370. Curr HIV Res. 2010. PMID: 20210780 Review.
-
Recent advances in the understanding of Jembrana disease.Vet Microbiol. 1995 Sep;46(1-3):249-55. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(95)00089-s. Vet Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8545963 Review.
References
-
- Bobrow, M. N., T. D. Harris, K. J. Shaughnessy, and G. J. Litt. 1989. Catalyzed reporter deposition, a novel method of signal amplification. Application to immunoassays. J. Immunol. Methods 125:279-285. - PubMed
-
- Bustin, S. A. 2002. Quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR): trends and problems. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 29:23-39. - PubMed
-
- Chadwick, B. J., R. J. Coelen, G. E. Wilcox, L. M. Sammels, and G. Kertayadnya. 1995. Nucleotide sequence analysis of Jembrana disease virus: a bovine lentivirus associated with an acute disease syndrome. J. Gen. Virol. 76:1637-1650. - PubMed
-
- Che, X. Y., L. W. Qiu, Y. X. Pan, K. Wen, W. Hao, L. Y. Zhang, Y. D. Wang, Z. Y. Liao, X. Hua, V. C. Cheng, and K. Y. Yuen. 2004. Sensitive and specific monoclonal antibody-based capture enzyme immunoassay for detection of nucleocapsid antigen in sera from patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:2629-2635. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

