Enhanced responsiveness to antigen contributes more to immunological memory in CD4 T cells than increases in the number of cells
- PMID: 16236121
- PMCID: PMC1802427
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02227.x
Enhanced responsiveness to antigen contributes more to immunological memory in CD4 T cells than increases in the number of cells
Abstract
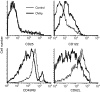
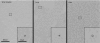
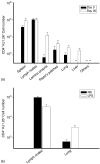
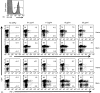
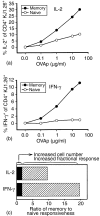
Although immunological memory is characterized by both an increase in the frequency of antigen-specific T cells and a qualitative change in the pattern of their subsequent response, it is not clear which of these components is more significant in the overall enhanced response to secondary stimulation. To address this question for the CD4+ T-cell response, T-cell receptor (TCR) Tg T cells were adoptively transferred to normal syngeneic mice that were immunized with the relevant peptide. After the initial expansion of TCR Tg T cells, the size of the subsequent memory population of T cells was approximately the same as the size of the starting population, independent of the number of TCR Tg cells initially transferred. This result was not caused by redistribution of memory cells into non-lymphoid tissues, although the relative frequency of antigen-specific T cells in these sites was increased after immunization. The fraction of the antigen specific TCR Tg cells that responded by production of either interleukin-2 or interferon-gammain vitro was substantially higher after immunization. Thus, the increased frequency of functionally responsive T cells was primarily caused by a higher fraction of responding T cells, rather than a substantial increase in the absolute number of antigen specific CD4+ TCR Tg T cells.
Figures
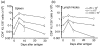


Similar articles
-
LFA-1 on CD4+ T cells is required for optimal antigen-dependent activation in vivo.J Immunol. 2004 Oct 1;173(7):4443-51. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.7.4443. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15383575
-
Instruction of naive CD4+ T cells by polarized CD4+ T cells within dendritic cell clusters.Eur J Immunol. 2003 Jun;33(6):1686-96. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323811. Eur J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12778487
-
Anti-CD3 priming generates heterogeneous antigen-specific memory CD4 T cells.Clin Immunol. 2005 Nov;117(2):125-32. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2005.07.012. Epub 2005 Sep 6. Clin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16143567
-
Bcl6 is essential for the generation of long-term memory CD4+ T cells.Int Immunol. 2007 Apr;19(4):427-33. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxm007. Epub 2007 Feb 16. Int Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17307796
-
Cognate CD4 help is essential for the reactivation and expansion of CD8 memory T cells directed against the hematopoietic cell-specific dominant minor histocompatibility antigen, H60.Blood. 2009 Apr 30;113(18):4273-80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-09-181263. Epub 2009 Jan 12. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19139082
Cited by
-
The potential of CD4 T-cell memory.Immunology. 2010 May;130(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03259.x. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20331470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct stimulation of tlr5+/+ CD11c+ cells is necessary for the adjuvant activity of flagellin.J Immunol. 2009 Jun 15;182(12):7539-47. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804225. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19494277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burnet FM. A modification of Jerne's theory of antibody production using the concept of clonal selection. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1957;20:67–9. - PubMed
-
- Topham DJ, Doherty PC. Longitudinal analysis of the acute Sendai virus-specific CD4+ T cell response and memory. J Immunol. 1998;161:4530–5. - PubMed
-
- Gebel HM, Scott JR, Parvin CA, Rodey GE. In vitro immunization to KLH. II. Limiting dilution analysis of antigen-reactive cells in primary and secondary culture. J Immunol. 1983;130:29–32. - PubMed
-
- Powers GD, Abbas AK, Miller RA. Frequencies of IL-2- and IL-4-secreting T cells in naive and antigen-stimulated lymphocyte populations. J Immunol. 1988;140:3352–7. - PubMed
-
- Ewing C, Topham DJ, Doherty PC. Prevalence and activation phenotype of Sendai virus-specific CD4+ T cells. Virology. 1995;210:179–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

