Inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase prevents mast cell activation and airway hyperresponsiveness
- PMID: 16192454
- PMCID: PMC2662982
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200503-361OC
Inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase prevents mast cell activation and airway hyperresponsiveness
Abstract
Rationale: Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) is important for Fc and B-cell receptor-mediated signaling.
Objective: To determine the activity of a specific Syk inhibitor (R406) on mast cell activation in vitro and on the development of allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) and inflammation in vivo.
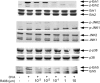
Methods: AHR and inflammation were induced after 10 d of allergen (ovalbumin [OVA]) exposure exclusively via the airways and in the absence of adjuvant. This approach was previously established to be IgE, FcepsilonRI, and mast cell dependent. Alternatively, mice were passively sensitized with OVA-specific IgE, followed by limited airway challenge. In vitro, the inhibitor was added to cultures of IgE-sensitized bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) before cross-linking with allergen.
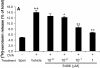
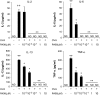
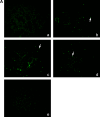
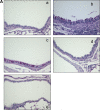
Results: The inhibitor prevented OVA-induced degranulation of passively IgE-sensitized murine BMMCs and inhibited the production of interleukin (IL)-13, tumor necrosis factor alpha, IL-2, and IL-6 in these sensitized BMMCs. When administered in vivo, R406 inhibited AHR, which developed in BALB/c mice exposed to aerosolized 1% OVA for 10 consecutive d (20 min/d), as well as pulmonary eosinophilia and goblet cell metaplasia. A similar inhibition of AHR was demonstrated in mice passively sensitized with OVA-specific IgE and exposed to limited airway challenge.
Conclusion: This study delineates a functional role for Syk in the development of mast cell- and IgE-mediated AHR and airway inflammation, and these results indicate that inhibition of Syk may be a target in the treatment of allergic asthma.
Figures
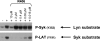

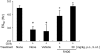


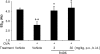
Similar articles
-
Syk activation in dendritic cells is essential for airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006 Apr;34(4):426-33. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0298OC. Epub 2005 Dec 9. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16339999 Free PMC article.
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition attenuates airway hyperresponsiveness and pollution-induced enhanced airway response in a chronic mouse model of asthma.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Feb;131(2):512-20.e1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.039. Epub 2012 Sep 13. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22981792
-
Inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase attenuates allergen-mediated airway constriction.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Dec;49(6):1085-92. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0200OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23889698
-
Role of IgE in the development of allergic airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness--a murine model.Allergy. 1999 Apr;54(4):297-305. doi: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.1999.00085.x. Allergy. 1999. PMID: 10371087 Review.
-
Syk kinase inhibitors in allergic diseases.Drug News Perspect. 2009 Apr;22(3):146-50. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2009.22.3.1354124. Drug News Perspect. 2009. PMID: 19440557 Review.
Cited by
-
SHP-1 regulation of mast cell function in allergic inflammation and anaphylaxis.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055763. Epub 2013 Feb 4. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23390550 Free PMC article.
-
IL-2 and IL-18 attenuation of airway hyperresponsiveness requires STAT4, IFN-gamma, and natural killer cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007 Mar;36(3):324-32. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0231OC. Epub 2006 Oct 12. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17038663 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase attenuates IgE-mediated airway contraction and mediator release in human precision cut lung slices.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Nov;173(21):3080-3087. doi: 10.1111/bph.13550. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27417329 Free PMC article.
-
Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition in the treatment of autoimmune, allergic and autoinflammatory diseases.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6):222. doi: 10.1186/ar3198. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 21211067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse innate stimuli activate basophils through pathways involving Syk and IκB kinases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 23;118(12):e2019524118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2019524118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33727419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Busse WW, Lemanske RF Jr. Asthma. N Engl J Med 2001;344:350–362. - PubMed
-
- Brightling CE, Bradding P, Symon FA, Holgate ST, Wardlaw AJ, Pavord ID. Mast-cell infiltration of airway smooth muscle in asthma. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1699–1705. - PubMed
-
- Luskova P, Draber P. Modulation of the Fcepsilon receptor I signaling by tyrosine kinase inhibitors: search for therapeutic targets of inflammatory and allergy diseases. Curr Pharm Des 2004;10:1727–1737. - PubMed
-
- Blank U, Rivera J. The ins and outs of IgE-dependent mast-cell exocytosis. Trends Immunol 2004;25:266–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

