Renewed interest in cancer immunotherapy with the tumor necrosis factor superfamily molecules
- PMID: 16187084
- PMCID: PMC11030687
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-005-0081-y
Renewed interest in cancer immunotherapy with the tumor necrosis factor superfamily molecules
Abstract
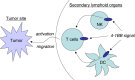
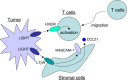
Molecules belonging to the Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) and TNF receptor superfamilies have explosively expanded through the era of genomics and bioinformatics. Biological investigations of these molecules have explored their potency as attractive targets for cancer therapy. Anti-tumor mechanisms mediated by TNF superfamily molecules (TNFSF) could be classified into direct actions onto tumor cells and indirect effects through immune or non-immune components of tumor-bearing host. In this review, we focus on TRAIL, CD40, 4-1BB (CD137), and LIGHT as promising molecules to mediate powerful and selective anti-tumor responses, and summarize their unique effector mechanisms. In addition, optimal approaches to manipulate these molecules for cancer therapy are also discussed. We try to provide an insight into a role of TNFSF in cancer therapeutics and highlight each of their potency to be an important player in anti-cancer strategies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular, structural, and biological characteristics of the tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily.Int J Clin Lab Res. 1996;26(3):143-59. doi: 10.1007/BF02592977. Int J Clin Lab Res. 1996. PMID: 8905447 Review.
-
The therapeutic potential of 4-1BB (CD137) in cancer.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005 Aug;5(5):357-63. doi: 10.2174/1568009054629681. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005. PMID: 16101383 Review.
-
4-1BB-specific monoclonal antibody promotes the generation of tumor-specific immune responses by direct activation of CD8 T cells in a CD40-dependent manner.J Immunol. 2002 Aug 15;169(4):1792-800. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.4.1792. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12165501
-
Increased gene expression of tumor necrosis factor superfamily ligands in peripheral blood mononuclear cells during chronic heart failure.Cardiovasc Res. 2002 Apr;54(1):175-82. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(02)00238-9. Cardiovasc Res. 2002. PMID: 12062373
-
Activation of c-jun N-terminal kinase by 4-1BB (CD137), a T cell co-stimulatory molecule.Mol Cells. 2000 Jun 30;10(3):247-52. Mol Cells. 2000. PMID: 10901161
Cited by
-
Increase in CD30 ligand/CD153 and TNF-alpha expressing mast cells in basal cell carcinoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2007 Sep;56(9):1407-15. doi: 10.1007/s00262-007-0290-7. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2007. PMID: 17268792 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-tumor effect of Liqi, a traditional Chinese medicine prescription, in tumor bearing mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2009 Jul 1;9:20. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-9-20. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2009. PMID: 19570195 Free PMC article.
-
Development and characterization of a potent immunoconjugate targeting the Fn14 receptor on solid tumor cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Jul;10(7):1276-88. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0161. Epub 2011 May 17. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21586630 Free PMC article.
-
Human single-nucleotide polymorphisms alter p53 sequence-specific binding at gene regulatory elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(1):178-89. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq764. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 20817676 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-delivered multimeric soluble CD40L DNA combined with Toll-Like Receptor agonists as a treatment for melanoma.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 8;4(10):e7334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007334. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19812695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afford SC, Randhawa S, Eliopoulos AG, Hubscher SG, Young LS, Adams DH. CD40 activation induces apoptosis in cultured human hepatocytes via induction of cell surface Fas ligand expression and amplifies Fas-mediated hepatocyte death during allograft rejection. J Exp Med. 1999;189:441–446. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.2.441. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asher A, Mule JJ, Reichert CM, Shiloni E, Rosenberg SA. Studies on the anti-tumor efficacy of systemically administered recombinant tumor necrosis factor against several murine tumors in vivo. J Immunol. 1987;138:963–974. - PubMed
-
- Browning JL, Sizing ID, Lawton P, Bourdon PR, Rennert PD, Majeau GR, Ambrose CM, Hession C, Miatkowski K, Griffiths DA, Ngam-ek A, Meier W, Benjamin CD, Hochman PS. Characterization of lymphotoxin-alpha beta complexes on the surface of mouse lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1997;159:3288–3298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

