ER stress-regulated translation increases tolerance to extreme hypoxia and promotes tumor growth
- PMID: 16148948
- PMCID: PMC1276162
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600777
ER stress-regulated translation increases tolerance to extreme hypoxia and promotes tumor growth
Abstract
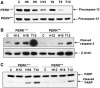
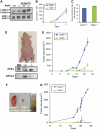
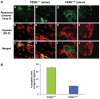
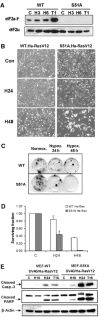
Tumor cell adaptation to hypoxic stress is an important determinant of malignant progression. While much emphasis has been placed on the role of HIF-1 in this context, the role of additional mechanisms has not been adequately explored. Here we demonstrate that cells cultured under hypoxic/anoxic conditions and transformed cells in hypoxic areas of tumors activate a translational control program known as the integrated stress response (ISR), which adapts cells to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Inactivation of ISR signaling by mutations in the ER kinase PERK and the translation initiation factor eIF2alpha or by a dominant-negative PERK impairs cell survival under extreme hypoxia. Tumors derived from these mutant cell lines are smaller and exhibit higher levels of apoptosis in hypoxic areas compared to tumors with an intact ISR. Moreover, expression of the ISR targets ATF4 and CHOP was noted in hypoxic areas of human tumor biopsy samples. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that activation of the ISR is required for tumor cell adaptation to hypoxia, and suggest that this pathway is an attractive target for antitumor modalities.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP Signaling Pathway in Tumor Progression During Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Curr Mol Med. 2016;16(6):533-44. doi: 10.2174/1566524016666160523143937. Curr Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27211800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4 module of the UPR in hypoxia resistance and tumor growth.Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Jul;5(7):723-8. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.7.2967. Epub 2006 Jul 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16861899 Review.
-
ER stress, hypoxia tolerance and tumor progression.Curr Mol Med. 2006 Feb;6(1):55-69. doi: 10.2174/156652406775574604. Curr Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16472113 Review.
-
Pollen Typhae Total Flavone Inhibits Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Human Aortic-Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells through Down-Regulating PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP Pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2019 Aug;25(8):604-612. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3052-4. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Chin J Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 30707413
-
Perk-dependent translational regulation promotes tumor cell adaptation and angiogenesis in response to hypoxic stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(24):9517-32. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01145-06. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17030613 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ablation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress kinase PERK induces paraptosis and type I interferon to promote anti-tumor T cell responses.Cancer Cell. 2022 Oct 10;40(10):1145-1160.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.08.016. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Cancer Cell. 2022. PMID: 36150390 Free PMC article.
-
Angiopoietin-like protein ANGPTL2 gene expression is correlated with lymph node metastasis in lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2012 Dec;4(6):1325-1328. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.924. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Oncol Lett. 2012. PMID: 23205131 Free PMC article.
-
ER residential chaperone GRP78 unconventionally relocalizes to the cell surface via endosomal transport.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jun;78(12):5179-5195. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03849-z. Epub 2021 May 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33974094 Free PMC article.
-
PERK utilizes intrinsic lipid kinase activity to generate phosphatidic acid, mediate Akt activation, and promote adipocyte differentiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jun;32(12):2268-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00063-12. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22493067 Free PMC article.
-
NQO1-induced activation of AMPK contributes to cancer cell death by oxygen-glucose deprivation.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 14;5:7769. doi: 10.1038/srep07769. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25586669 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiri G, Nahari D, Finkelstein Y, Le SY, Elroy-Stein O, Levi BZ (1998) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression is mediated by internal initiation of translation and alternative initiation of transcription. Oncogene 17: 227–236 - PubMed
-
- Ameri K, Lewis CE, Raida M, Sowter H, Hai T, Harris AL (2004) Anoxic induction of ATF-4 through HIF-1-independent pathways of protein stabilization in human cancer cells. Blood 103: 1876–1882 - PubMed
-
- Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2: 326–332 - PubMed
-
- Blouw B, Song H, Tihan T, Bosze J, Ferrara N, Gerber HP, Johnson RS, Bergers G (2003) The hypoxic response of tumors is dependent on their microenvironment. Cancer Cell 4: 133–146 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

