The human herpesvirus 6 G protein-coupled receptor homolog U51 positively regulates virus replication and enhances cell-cell fusion in vitro
- PMID: 16140767
- PMCID: PMC1212626
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.18.11914-11924.2005
The human herpesvirus 6 G protein-coupled receptor homolog U51 positively regulates virus replication and enhances cell-cell fusion in vitro
Abstract
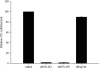
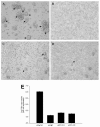
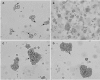
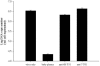
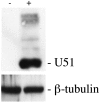
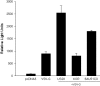
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) is a ubiquitous T-lymphotropic betaherpesvirus that encodes two G protein-coupled receptor homologs, U12 and U51. HHV-6A U51 has been reported to bind to CC chemokines including RANTES, but the biological function of U51 remains uncertain. In this report, we stably expressed short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) specific for U51 in human T cells and then infected these cells with HHV-6. Viral DNA replication was reduced 50-fold by the U51 siRNA, and virally induced cytopathic effects were also inhibited. In contrast, viral replication and syncytium formation were unaltered in cells that expressed a scrambled derivative of the siRNA or an irrelevant siRNA and were restored to normal when a human codon-optimized derivative of U51 was introduced into cells containing the U51 siRNA. To examine the mechanism whereby U51 might contribute to viral replication, we explored the signaling characteristics of U51. None of the chemokines and opioids tested was able to induce G protein coupling by U51, and no evidence for opioid ligand binding by U51 was obtained. The effect of U51 on cell-cell fusion was also evaluated; these studies showed that U51 enhanced cell fusion mediated by the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. However, a U51-specific antiserum had no virus-neutralizing activity, suggesting that U51 may not be involved in the initial interaction between the virus particle and host cell. Overall, these studies suggest that HHV-6 U51 is a positive regulator of virus replication in vitro, perhaps because it may promote membrane fusion and facilitates cell-cell spread of this highly cell-associated virus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RANTES binding and down-regulation by a novel human herpesvirus-6 beta chemokine receptor.J Immunol. 2000 Mar 1;164(5):2396-404. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2396. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10679075
-
Human herpesvirus 7 open reading frames U12 and U51 encode functional beta-chemokine receptors.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(11):7068-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.11.7068-7076.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15890946 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine-directed trafficking of receptor stimulus to different g proteins: selective inducible and constitutive signaling by human herpesvirus 6-encoded chemokine receptor U51.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;69(3):888-98. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.015222. Epub 2005 Dec 6. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16332987
-
Recent topics related to human herpesvirus 6 cell tropism.Cell Microbiol. 2009 Jul;11(7):1001-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2009.01312.x. Epub 2009 Mar 12. Cell Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19290911 Review.
-
Molecular biology of human herpesviruses 6A and 6B.Infect Agents Dis. 1993 Dec;2(6):343-60. Infect Agents Dis. 1993. PMID: 8012736 Review.
Cited by
-
From Viral Infection to Autoimmune Reaction: Exploring the Link between Human Herpesvirus 6 and Autoimmune Diseases.Microorganisms. 2024 Feb 9;12(2):362. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020362. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HHV-6 Infection and Chemokine RANTES Signaling Pathway Disturbance in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis.Viruses. 2020 Jun 26;12(6):689. doi: 10.3390/v12060689. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32604892 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesvirus 6A infection and immunopathogenesis in humanized Rag2⁻/⁻ γc⁻/⁻ mice.J Virol. 2013 Nov;87(22):12020-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01556-13. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24006442 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokines in Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs).Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 6;11(6):847. doi: 10.3390/biom11060847. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34204146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms deployed by virally encoded G protein-coupled receptors in human diseases.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;53:331-54. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010510-100608. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23092247 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ablashi, D. V., N. Balachandran, S. F. Josephs, C. L. Hung, G. R. Krueger, B. Kramarsky, S. Z. Salahuddin, and R. C. Gallo. 1991. Genomic polymorphism, growth properties, and immunologic variations in human herpesvirus-6 isolates. Virology 184:545-552. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib, G., C. Combadiere, C. C. Broder, Y. Feng, P. E. Kennedy, P. M. Murphy, and E. A. Berger. 1996. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science 272:1955-1958. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitakis, L., E. Geras-Raaka, A. Varma, M. C. Gershengorn, and E. Cesarman. 1997. Human herpesvirus KSHV encodes a constitutively active G-protein-coupled receptor linked to cell proliferation. Nature 385:347-350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

