Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B binds to cell surfaces independently of heparan sulfate and blocks virus entry
- PMID: 16140736
- PMCID: PMC1212636
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.18.11588-11597.2005
Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B binds to cell surfaces independently of heparan sulfate and blocks virus entry
Abstract
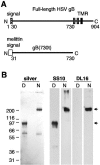
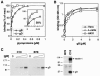
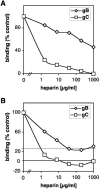
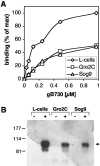
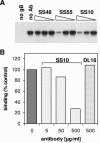
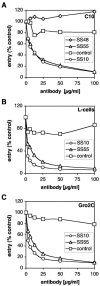
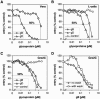
Virion glycoproteins gB, gD, and gH/gL play essential roles for herpes simplex virus (HSV) entry. The function of gD is to interact with a cognate receptor, and soluble forms of gD block HSV entry by tying up cell surface receptors. Both gB and the nonessential gC interact with cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG), promoting viral attachment. However, cells deficient in proteoglycan synthesis can still be infected by HSV. This suggests another function for gB. We found that a soluble truncated form of gB bound saturably to the surface of Vero, A431, HeLa, and BSC-1 cells, L-cells, and a mouse melanoma cell line expressing the gD receptor nectin-1. The HSPG analog heparin completely blocked attachment of the gC ectodomain to Vero cells. In contrast, heparin only partially blocked attachment of soluble gB, leaving 20% of the input gB still bound even at high concentrations of inhibitor. Moreover, heparin treatment removed soluble gC but not gB from the cell surface. These data suggest that a portion of gB binds to cells independently of HSPG. In addition, gB bound to two HSPG-deficient cell lines derived from L-cells. Gro2C cells are deficient in HSPG, and Sog9 cells are deficient in HSPG, as well as chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG). To identify particular gB epitopes responsible for HSPG-independent binding, we used a panel of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to gB to block gB binding. Only those gB MAbs that neutralized virus blocked binding of soluble gB to the cells. HSV entry into Gro2C and Sog9 cells was reduced but still detectable relative to the parental L-cells, as previously reported. Importantly, entry into Gro2C cells was blocked by purified forms of either the gD or gB ectodomain. On a molar basis, the extent of inhibition by gB was similar to that seen with gD. Together, these results suggest that soluble gB binds specifically to the surface of different cell types independently of HSPG and CSPG and that by doing so, the protein inhibits entry. The results provide evidence for the existence of a cellular entry receptor for gB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gC with mammalian cell surface molecules.J Virol. 1995 Jul;69(7):4471-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.7.4471-4483.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7769707 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal antibodies to distinct sites on herpes simplex virus (HSV) glycoprotein D block HSV binding to HVEM.J Virol. 1998 May;72(5):3595-601. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.5.3595-3601.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9557640 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function analysis of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B with fusion-from-without activity.Virology. 2008 Dec 20;382(2):207-16. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.09.015. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18950828
-
Herpes simplex virus: receptors and ligands for cell entry.Cell Microbiol. 2004 May;6(5):401-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00389.x. Cell Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15056211 Review.
-
The role of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the virus replication cycle.Acta Virol. 1998 Apr;42(2):103-18. Acta Virol. 1998. PMID: 9770079 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytomegalovirus UL131-128 products promote gB conformational transition and gB-gH interaction during entry into endothelial cells.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(20):11479-88. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00788-07. Epub 2007 Aug 8. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17686875 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives on Different Steps of Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 In Vitro Replicative Cycle.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 23;23(15):8135. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158135. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897709 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoprotein C Regulates Low-pH Entry.mSphere. 2020 Feb 5;5(1):e00826-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00826-19. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32024702 Free PMC article.
-
Topical herpes simplex virus 2 (HSV-2) vaccination with human papillomavirus vectors expressing gB/gD ectodomains induces genital-tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells and reduces genital disease and viral shedding after HSV-2 challenge.J Virol. 2015 Jan;89(1):83-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02380-14. Epub 2014 Oct 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25320297 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gH/gL and gB bind Toll-like receptor 2, and soluble gH/gL is sufficient to activate NF-κB.J Virol. 2012 Jun;86(12):6555-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00295-12. Epub 2012 Apr 11. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22496225 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akula, S. M., N. P. Pramod, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2002. Integrin α3β1 (CD 49c/29) is a cellular receptor for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) entry into the target cells. Cell 108:407-419. - PubMed
-
- Banfield, B. W., Y. Leduc, L. Esford, R. J. Visalli, C. R. Brandt, and F. Tufaro. 1995. Evidence for an interaction of herpes simplex virus with chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans during infection. Virology 208:531-539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

