Automation of gene assignments to metabolic pathways using high-throughput expression data
- PMID: 16135255
- PMCID: PMC1239907
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-217
Automation of gene assignments to metabolic pathways using high-throughput expression data
Abstract
Background: Accurate assignment of genes to pathways is essential in order to understand the functional role of genes and to map the existing pathways in a given genome. Existing algorithms predict pathways by extrapolating experimental data in one organism to other organisms for which this data is not available. However, current systems classify all genes that belong to a specific EC family to all the pathways that contain the corresponding enzymatic reaction, and thus introduce ambiguity.
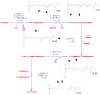
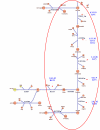
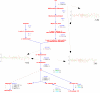
Results: Here we describe an algorithm for assignment of genes to cellular pathways that addresses this problem by selectively assigning specific genes to pathways. Our algorithm uses the set of experimentally elucidated metabolic pathways from MetaCyc, together with statistical models of enzyme families and expression data to assign genes to enzyme families and pathways by optimizing correlated co-expression, while minimizing conflicts due to shared assignments among pathways. Our algorithm also identifies alternative ("backup") genes and addresses the multi-domain nature of proteins. We apply our model to assign genes to pathways in the Yeast genome and compare the results for genes that were assigned experimentally. Our assignments are consistent with the experimentally verified assignments and reflect characteristic properties of cellular pathways.
Conclusion: We present an algorithm for automatic assignment of genes to metabolic pathways. The algorithm utilizes expression data and reduces the ambiguity that characterizes assignments that are based only on EC numbers.
Figures
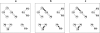

Similar articles
-
Expectation-maximization algorithms for fuzzy assignment of genes to cellular pathways.Comput Syst Bioinformatics Conf. 2006:281-91. Comput Syst Bioinformatics Conf. 2006. PMID: 17369646
-
Bayesian Orthogonal Least Squares (BOLS) algorithm for reverse engineering of gene regulatory networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Jul 13;8:251. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-251. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17626641 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative inference of dynamic regulatory pathways via microarray data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Mar 7;6:44. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-44. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15748298 Free PMC article.
-
State space modeling of yeast gene expression dynamics.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2007 Feb;5(1):31-46. doi: 10.1142/s0219720007002515. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2007. PMID: 17477490
-
Co-expression analysis of metabolic pathways in plants.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;553:247-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-563-7_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19588109 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolomic network analysis of estrogen-stimulated MCF-7 cells: a comparison of overrepresentation analysis, quantitative enrichment analysis and pathway analysis versus metabolite network analysis.Arch Toxicol. 2017 Jan;91(1):217-230. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1695-x. Epub 2016 Apr 2. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27039105 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics of Nitrogen Cycling Pathways in Bacteria and Archaea.Microb Ecol. 2019 Apr;77(3):597-606. doi: 10.1007/s00248-018-1239-4. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Microb Ecol. 2019. PMID: 30105504
-
Missing gene identification using functional coherence scores.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 24;6:31725. doi: 10.1038/srep31725. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27552989 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of biochemical networks in microorganisms.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009 Feb;7(2):129-43. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1949. Epub 2008 Dec 31. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19116616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MORPH algorithm: ranking candidate genes for membership in Arabidopsis and tomato pathways.Plant Cell. 2012 Nov;24(11):4389-406. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.104513. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 23204403 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

