Membrane metabolism mediated by Sec14 family members influences Arf GTPase activating protein activity for transport from the trans-Golgi
- PMID: 16126894
- PMCID: PMC1200303
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506156102
Membrane metabolism mediated by Sec14 family members influences Arf GTPase activating protein activity for transport from the trans-Golgi
Abstract
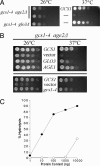
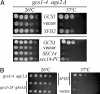
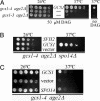
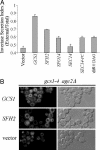
The budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains a family of Arf (ADP-ribosylation factor) GTPase activating protein (GAP) proteins with the Gcs1 + Age2 ArfGAP pair providing essential overlapping function for the movement of transport vesicles from the trans-Golgi network. We have generated a temperature-sensitive but stable version of the Gcs1 protein that is impaired only for trans-Golgi transport and find that deleterious effects of this enfeebled Gcs1-4 mutant protein are relieved by increased gene dosage of the gcs1-4 mutant gene itself or by the SFH2 gene (also called CSR1), encoding a phosphatidylinositol transfer protein (PITP). This effect was not seen for the SEC14 gene, encoding the founding member of the yeast PITP protein family, even though the Gcs1 and Age2 ArfGAPs are known to be downstream effectors of Sec14-mediated activity for trans-Golgi transport. Sfh2-mediated suppression of inadequate Gcs1-4 function depended on phospholipase D, whereas inadequate Gcs1-4 activity was relieved by increasing levels of diacylglycerol (DAG). Recombinant Gcs1 protein was found to bind certain phospholipids but not DAG. Our findings favor a model of Gcs1 localization through binding to specific phospholipids and activation of ArfGAP activity by DAG-mediated membrane curvature as the transport vesicle is formed. Thus, ArfGAPs are subject to both temporal and spatial regulation that is facilitated by Sfh2-mediated modulation of the lipid environment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The yeast Arf GTPase-activating protein Age1 is regulated by phospholipase D for post-Golgi vesicular transport.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 18;286(7):5187-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.185108. Epub 2010 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21135091 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of specific lipid-regulated ADP ribosylation factor-GTPase-activating proteins is required for Sec14p-dependent Golgi secretory function in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Jul;13(7):2193-206. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-11-0563.. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12134061 Free PMC article.
-
Retrograde transport from the yeast Golgi is mediated by two ARF GAP proteins with overlapping function.EMBO J. 1999 Feb 1;18(3):555-64. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.3.555. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 9927415 Free PMC article.
-
Surprising roles for phospholipid binding proteins revealed by high throughput genetics.Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;88(4):565-74. doi: 10.1139/O09-171. Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20651827 Review.
-
Sec14 like PITPs couple lipid metabolism with phosphoinositide synthesis to regulate Golgi functionality.Subcell Biochem. 2012;59:271-87. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-3015-1_9. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22374094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulated Arl1, a regulator of post-Golgi vesicle tethering, can inhibit endosomal transport and cell proliferation in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jul 1;22(13):2337-47. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-09-0765. Epub 2011 May 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21562219 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of yeast polarized exocytosis by phosphoinositide lipids.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Nov 19;81(1):457. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05483-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39560727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chs5/6 complex: a multiprotein complex that interacts with and conveys chitin synthase III from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Oct;17(10):4157-66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-03-0210. Epub 2006 Jul 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16855022 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicle trafficking from a lipid perspective: Lipid regulation of exocytosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Cell Logist. 2012 Jul 1;2(3):151-160. doi: 10.4161/cl.20490. Cell Logist. 2012. PMID: 23181198 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of phosphoinositide levels by the phospholipid transfer protein Sec14p controls Cdc42p/p21-activated kinase-mediated cell cycle progression at cytokinesis.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Oct;6(10):1814-23. doi: 10.1128/EC.00087-07. Epub 2007 Jun 29. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17601877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kirchhausen, T. (2000) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1, 187–198. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson, J. G. & Klausner, R. D. (1994) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 6, 527–532. - PubMed
-
- Peyroche, A., Paris, S. & Jackson, C. L. (1996) Nature 384, 479–481. - PubMed
-
- Cukierman, E., Huber, I., Rotman, M. & Cassel, D. (1995) Science 270, 1999–2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

