Defunctionalized lobeline analogues: structure-activity of novel ligands for the vesicular monoamine transporter
- PMID: 16107155
- PMCID: PMC3617589
- DOI: 10.1021/jm0501228
Defunctionalized lobeline analogues: structure-activity of novel ligands for the vesicular monoamine transporter
Abstract
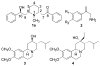
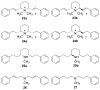
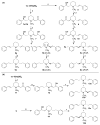
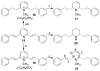
(-)-Lobeline (2R,6S,10S), an antagonist at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), inhibits the neurochemical and behavioral effects of methamphetamine and inhibits dopamine transporter (DAT) and vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT2) function. VMAT2 is a target for the development of treatments for methamphetamine abuse. Structural modification of lobeline affords the defunctionalized analogues meso-transdiene (MTD) and lobelane, which have high potency and selectivity for VMAT2. To establish the structure-activity relationships within this novel class of VMAT2 ligands, specific stereochemical forms of MTD, lobelane, and other structurally related analogues have been synthesized. These compounds have been evaluated for inhibition of [(3)H]nicotine ([(3)H]NIC) binding (alpha4beta2 nAChR), [(3)H]methyllycaconitine ([(3)H]MLA) binding (alpha7 nAChR), and [(3)H]dihydrotetrabenazine ([(3)H]DTBZ) binding (VMAT2). Generally, all of these analogues had lower affinities at alpha4beta2 and alpha7 nAChRs compared to lobeline, thereby increasing selectivity for VMAT2. The following structural modifications resulted in only modest changes in affinity for VMAT2, affording analogues that were less potent than the lead compound, lobelane: (1) altering the stereochemistry at the C-2 and C-6 positions of the piperidino ring, (2) varying unsaturation in the piperidino C-2 and C-6 substituents, (3) introducing unsaturation into the piperidine ring, (4) ring-opening or eliminating the piperidine ring, and (5) removing the piperidino N-methyl group. Furthermore, incorporating a quaternary ammonium group into defunctionalized lobeline molecules in the cis-series resulted in significant loss of affinity for VMAT2, whereas only a modest change in affinity was obtained in the trans-series. The most potent (K(i) = 630 nM) and VMAT2-selective compound evaluated was the N-methyl-2,6-cis-bis(naphthaleneethyl)piperidine analogue (1-NAP-lobelane), in which the phenyl groups of lobelane were replaced with 1-naphthyl moieties. Thus, initial structure-activity relationship studies reveal that the most promising structural changes to the lobeline molecule that lead to enhancement of VMAT2 affinity and selectivity are defunctionalization, affording lobelane and MTD, and replacement of the phenyl rings of lobelane with other aromatic moieties that have a pi-extended structure.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis and interaction at the vesicular monoamine transporter-2 of lobeline analogs: potential pharmacotherapies for the treatment of psychostimulant abuse.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(9):1103-27. doi: 10.2174/156802611795371332. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21050177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lobeline analogs with enhanced affinity and selectivity for plasmalemma and vesicular monoamine transporters.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Sep;310(3):1035-45. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.068098. Epub 2004 Apr 30. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004. PMID: 15121762
-
Lobelane inhibits methamphetamine-evoked dopamine release via inhibition of the vesicular monoamine transporter-2.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Feb;332(2):612-21. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.160275. Epub 2009 Oct 23. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 19855096 Free PMC article.
-
Phenyl ring-substituted lobelane analogs: inhibition of [³H]dopamine uptake at the vesicular monoamine transporter-2.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Mar;336(3):724-33. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.172882. Epub 2010 Sep 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 20876747 Free PMC article.
-
The vesicular monoamine transporter-2: an important pharmacological target for the discovery of novel therapeutics to treat methamphetamine abuse.Adv Pharmacol. 2014;69:71-106. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420118-7.00002-0. Adv Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24484975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel N-1,2-dihydroxypropyl analogs of lobelane inhibit vesicular monoamine transporter-2 function and methamphetamine-evoked dopamine release.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Oct;339(1):286-97. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.184770. Epub 2011 Jul 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21778282 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and interaction at the vesicular monoamine transporter-2 of lobeline analogs: potential pharmacotherapies for the treatment of psychostimulant abuse.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(9):1103-27. doi: 10.2174/156802611795371332. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21050177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of novel azetidine analogs as potent inhibitors of vesicular [3H]dopamine uptake.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Nov 1;21(21):6771-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Aug 11. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23993667 Free PMC article.
-
(E,E)-1-Methyl-2,6-distyrylpyridinium iodide.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010 Jun 26;66(Pt 7):o1793. doi: 10.1107/S1600536810018519. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010. PMID: 21588003 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of symmetrical 1,5-disubstituted granatanines.Tetrahedron Lett. 2008 Oct 27;49(44):6330-6333. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.08.066. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008. PMID: 23678188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wise RA, Bozarth MA. A psychomotor stimulant theory of addiction. Psychol Rev. 1987;94:469–492. - PubMed
-
- Koob GF. Neural mechanisms of drug reinforcement. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1992;654:171–191. - PubMed
-
- Fleckenstein AE, Hanson GR. Impact of psychostimulants on vesicular monoamine transporter function. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;479:283–289. - PubMed
-
- Brown JM, Hanson GR, Fleckenstein AE. Methamphetamine rapidly decrease vesicular dopamine uptake. J Neurochem. 2000;74:2221–2223. - PubMed
-
- Brown JM, Hanson GR, Fleckenstein AE. Regulation of the vesicular monoamine transporter-2: A novel mechanism for cocaine and other psychostimulants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;296:762–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

