Osteoclast responses to lipopolysaccharide, parathyroid hormone and bisphosphonates in neonatal murine calvaria analyzed by laser scanning confocal microscopy
- PMID: 16087705
- PMCID: PMC3957542
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.5A6630.2005
Osteoclast responses to lipopolysaccharide, parathyroid hormone and bisphosphonates in neonatal murine calvaria analyzed by laser scanning confocal microscopy
Abstract
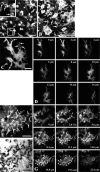
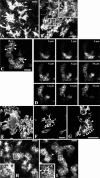
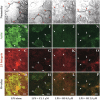
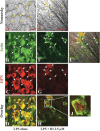
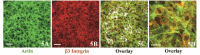
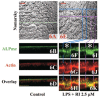
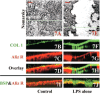
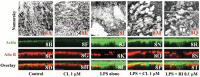
Because the development and activity of osteoclasts in bone remodeling is critically dependent on cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, we used laser confocal microscopy to study the response of osteoclasts to lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 10 microg/ml), parathyroid hormone (PTH; 10(-8) M), and bisphosphonates (BPs; 1-25 microM clodronate or 0.1-2.5 microM risedronate) in cultured neonatal calvaria. Following treatment with LPS or PTH (<48 hr), osteopontin (OPN) and the alphavbeta3 integrin were found colocalized with the actin ring in the sealing zone of actively resorbing osteoclasts. In contrast, non-resorbing osteoclasts in BP-treated cultures showed morphological abnormalities, including retraction of pseudopods and vacuolization of cytoplasm. In the combined presence of LPS and BP, bone-resorbing osteoclasts were smaller and the sealing zone diffuse, reflecting reduced actin, OPN, and beta3 integrin staining. Depth analyses of calvaria showed that the area of resorbed bone was filled with proliferating osteoblastic cells that stained for alkaline phosphatase, collagen type I, and bone sialoprotein, regardless of the presence of BPs. These studies show that confocal microscopy of neonatal calvaria in culture can be used to assess the cytological relationships between osteoclasts and osteoblastic cells in response to agents that regulate bone remodeling in situ, avoiding systemic effects that can compromise in vivo studies and artifacts associated with studies of isolated osteoclasts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current topics in pharmacological research on bone metabolism: inhibitory effects of bisphosphonates on the differentiation and activity of osteoclasts.J Pharmacol Sci. 2006 Mar;100(3):189-94. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fmj05004x2. Epub 2006 Mar 4. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16518076 Review.
-
Visualizing mineral binding and uptake of bisphosphonate by osteoclasts and non-resorbing cells.Bone. 2008 May;42(5):848-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2007.12.225. Epub 2008 Jan 26. Bone. 2008. PMID: 18325866
-
Risedronate activity in the fetal and neonatal mouse.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993 Oct;109(4):623-33. doi: 10.1177/019459989310900401. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1993. PMID: 8233497
-
Isolation of human osteoclasts formed in vitro: hormonal effects on the bone-resorbing activity of human osteoclasts.Calcif Tissue Int. 2002 Dec;71(6):539-46. doi: 10.1007/s00223-001-2128-1. Epub 2002 Sep 18. Calcif Tissue Int. 2002. PMID: 12232680
-
Regulatory mechanism of osteoclast activation.J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2003;52(6):527-33. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/52.6.527. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2003. PMID: 14756240 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-resorptive agents reduce the size of resorption cavities: a three-dimensional dynamic bone histomorphometry study.Bone. 2013 Nov;57(1):277-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.08.018. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Bone. 2013. PMID: 23988275 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering of pattern recognition receptors for fungal detection.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Feb 20;10(2):e1003873. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003873. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24586145 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Structure-Dependent Effects of Bisphosphonates on Inflammatory Responses in Cultured Neonatal Mouse Calvaria.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jun 9;9(6):503. doi: 10.3390/antiox9060503. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32526922 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients with multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia: a retrospective multicentric study.Blood Cancer J. 2012 Mar;2(3):e62. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2012.9. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Blood Cancer J. 2012. PMID: 22829257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson G, Johansson EK. (1996) Adhesion of human myelomonocytic (HL-60) cells induced by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and phorbol myristate acetate is dependent on osteopontin synthesis and the alpha v beta 3 integrin. Connect Tissue Res 35: 163–171 - PubMed
-
- Burdi AR. (1965) Toluidine Blue-Alizarin Red S staining of cartilage and bone in whole-mount skeletons in vitro. Stain Technol 40: 45–48 - PubMed
-
- Cecchini MG, Fleisch H. (1990) Bisphosphonates in vitro specifically inhibit, among the hematopoietic series, the development of the mouse mononuclear phagocyte lineage. J Bone Miner Res 5: 1019–1027 - PubMed
-
- Chellaiah MA, Hruska KA. (2003) The integrin alpha(v)beta(3) and CD44 regulate the actions of osteopontin on osteoclast motility. Calcif Tissue Int 72: 197–205 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

