Primary sooty mangabey simian immunodeficiency virus and human immunodeficiency virus type 2 nef alleles modulate cell surface expression of various human receptors and enhance viral infectivity and replication
- PMID: 16051847
- PMCID: PMC1182674
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10547-10560.2005
Primary sooty mangabey simian immunodeficiency virus and human immunodeficiency virus type 2 nef alleles modulate cell surface expression of various human receptors and enhance viral infectivity and replication
Abstract
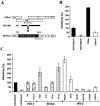
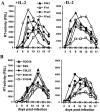
The nef gene of the pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) mac239 clone has been well characterized. Little is known, however, about the function of nef alleles derived from naturally SIVsm-infected sooty mangabeys (Cercocebus atys) and from human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2)-infected individuals. Addressing this, we demonstrate that, similarly to the SIVmac239 nef, primary SIVsm and HIV-2 nef alleles down-modulate cell surface expression of human CD4, CD28, CD3, and class I or II major histocompatibility complex (MHC-I or MHC-II, respectively) molecules, up-regulate surface expression of the invariant chain (Ii) associated with immature MHC-II, inhibit early T-cell activation events, and enhance virion infectivity. Both also stimulate viral replication, although HIV-2 nef alleles were less active in this assay than SIVsm nef alleles. Mutational analysis showed that a dileucine-based sorting motif in the C-proximal loop of SIV or HIV-2 Nef is critical for its effects on CD4, CD28, and Ii but dispensable for down-regulation of CD3, MHC-I, and MHC-II. The C terminus of SIV and HIV-2 Nef was exclusively required for down-modulation of MHC-I, further demonstrating that analogous functions are mediated by different domains in Nef proteins derived from different groups of primate lentiviruses. Our results demonstrate that none of the eight Nef functions investigated had been newly acquired after cross-species transmission of SIVsm from naturally infected mangabeys to humans or macaques. Notably, HIV-2 and SIVsm nef alleles efficiently down-modulate CD3 and C28 surface expression and inhibit T-cell activation more efficiently than HIV-1 nef alleles. These differences in Nef function might contribute to the relatively low levels of immune activation observed in HIV-2-infected human individuals.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Primary SIVsm isolates use the CCR5 coreceptor from sooty mangabeys naturally infected in west Africa: a comparison of coreceptor usage of primary SIVsm, HIV-2, and SIVmac.Virology. 1998 Jun 20;246(1):113-24. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9174. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9656999
-
Nef alleles from children with non-progressive HIV-1 infection modulate MHC-II expression more efficiently than those from rapid progressors.AIDS. 2007 May 31;21(9):1103-7. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32816aa37c. AIDS. 2007. PMID: 17502720
-
Specific suppression of human CD4 surface expression by Nef from the pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239open.Virology. 1994 Jun;201(2):373-9. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1303. Virology. 1994. PMID: 8184546
-
The function of simian chemokine receptors in the replication of SIV.Semin Immunol. 1998 Jun;10(3):215-23. doi: 10.1006/smim.1998.0135. Semin Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9653048 Review.
-
Naturally SIV-infected sooty mangabeys: are we closer to understanding why they do not develop AIDS?J Med Primatol. 2005 Oct;34(5-6):243-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0684.2005.00122.x. J Med Primatol. 2005. PMID: 16128919 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient Nef-mediated downmodulation of TCR-CD3 and CD28 is associated with high CD4+ T cell counts in viremic HIV-2 infection.J Virol. 2012 May;86(9):4906-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06856-11. Epub 2012 Feb 15. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22345473 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Nef with p21-activated kinase 2 is dispensable for efficient human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication and cytopathicity in ex vivo-infected human lymphoid tissue.J Virol. 2007 Dec;81(23):13005-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01436-07. Epub 2007 Sep 19. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17881449 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-induced immune activation: pathogenesis and clinical relevance - summary of a workshop organized by the German AIDS Society (DAIG e.v.) and the ICH Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, November 22, 2008.Eur J Med Res. 2010 Jan 29;15(1):1-12. doi: 10.1186/2047-783x-15-1-1. Eur J Med Res. 2010. PMID: 20159665 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of T-cell receptor-induced actin remodeling and relocalization of Lck are evolutionarily conserved activities of lentiviral Nef proteins.J Virol. 2009 Nov;83(22):11528-39. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01423-09. Epub 2009 Sep 2. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19726522 Free PMC article.
-
The inability to disrupt the immunological synapse between infected human T cells and APCs distinguishes HIV-1 from most other primate lentiviruses.J Clin Invest. 2009 Oct;119(10):2965-75. doi: 10.1172/JCI38994. Epub 2009 Sep 14. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19759518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arganaraz, E. R., M. Schindler, F. Kirchhoff, M. J. Cortes, and J. Lama. 2003. Enhanced CD4 down-modulation by late stage HIV-1 nef alleles is associated with increased Env incorporation and viral replication. J. Biol. Chem. 278:33912-33919. - PubMed
-
- Bell, I., C. Ashman, J. Maughan, E. Hooker, F. Cook, and T. A. Reinhart. 1998. Association of simian immunodeficiency virus Nef with the T-cell receptor (TCR) zeta chain leads to TCR down-modulation. J. Gen. Virol. 79:2717-2727. - PubMed
-
- Blagoveshchenskaya, A. D., L. Thomas, S. F. Feliciangeli, C. H. Hung, and G. Thomas. 2002. HIV-1 Nef downregulates MHC-I by a PACS-1- and PI3K-regulated ARF6 endocytic pathway. Cell 111:853-866. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

