Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3A domains essential for growth of lymphoblasts: transcriptional regulation through RBP-Jkappa/CBF1 is critical
- PMID: 16051810
- PMCID: PMC1182629
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10171-10179.2005
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3A domains essential for growth of lymphoblasts: transcriptional regulation through RBP-Jkappa/CBF1 is critical
Abstract
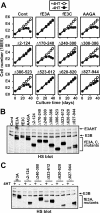
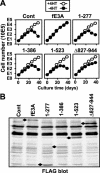
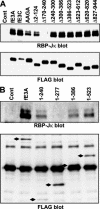
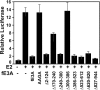
Experimental reverse genetic replacement of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3A (EBNA3A) with a conditional mutant EBNA3A revealed that EBNA3A is critical for continued lymphoblastoid cell (LCL) growth. Wild-type (wt) EBNA3A expressed in the LCLs specifically sustained growth under nonpermissive conditions, whereas EBNA3B or EBNA3C expression had no effect (S. Mauro, E. Johannsen, D. Illanes, A. Cooper, and E. Kieff, J. Virol. 77:10437-10447, 2003). This genetic system and related biochemical assays have now been used to discover that EBNA3A lacking amino acid residues 170 to 240 (delta170-240), TLGC202 to AAGA202, or delta300-386, which are deficient in repression of EBNA2 activation of an RBP-Jkappa/CBF1-dependent EBV Cp enhancer, are null mutations for LCL growth, whereas EBNA3A delta2-124, delta410-439, delta440-470, delta470-500, delta500-523, delta523-612, and delta620-820, which are wt in repression are wt for LCL growth. Thus, EBNA3A regulation of transcription through RBP-Jkappa/CBF1 is critical for LCL growth. EBNA3A mutants deleted of amino acid residues 240 to 300, 386 to 410, or 827 to 944 were intermediate, null, or intermediate, respectively, for LCL growth despite being wt for RBP-Jkappa association and repression. Amino acid residues 240 to 300, 386 to 410, and, particularly, C-terminal residues 827 to 944 are therefore likely to contribute to LCL growth through RBP-Jkappa-independent mechanisms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EBNA3A association with RBP-Jkappa down-regulates c-myc and Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblast growth.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(2):999-1010. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.2.999-1010.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12502816 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional repression by the Epstein-Barr virus EBNA3A protein tethered to DNA does not require RBP-Jkappa.J Gen Virol. 1998 Feb;79 ( Pt 2):363-70. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-79-2-363. J Gen Virol. 1998. PMID: 9472621
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein EBNA3C residues critical for maintaining lymphoblastoid cell growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 17;106(11):4419-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813134106. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19237563 Free PMC article.
-
[Transcriptional activity of EBNA2 through RBP-J].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Feb;55(2):293-8. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9046813 Review. Japanese.
-
EBNA2 and Notch signalling in Epstein-Barr virus mediated immortalization of B lymphocytes.Semin Cancer Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):423-34. doi: 10.1006/scbi.2001.0409. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001. PMID: 11669604 Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction of MEQ protein and C-terminal-binding protein is critical for induction of lymphomas by Marek's disease virus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 7;103(6):1687-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507595103. Epub 2006 Jan 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16446447 Free PMC article.
-
The nucleotide polymorphisms within the Epstein-Barr virus C and Q promoters from nasopharyngeal carcinoma affect transcriptional activity in vitro.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Mar;269(3):931-8. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1862-x. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22146864
-
Methylation status and AP1 elements are involved in EBV-mediated miR-155 expression in EBV positive lymphoma cells.Virology. 2016 Jul;494:158-67. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27110708 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin profiling of Epstein-Barr virus latency control region.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(12):6389-401. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02172-06. Epub 2007 Apr 4. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17409162 Free PMC article.
-
The Cooperative Functions of the EBNA3 Proteins Are Central to EBV Persistence and Latency.Pathogens. 2018 Mar 17;7(1):31. doi: 10.3390/pathogens7010031. Pathogens. 2018. PMID: 29562595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alfieri, C., M. Birkenbach, and E. Kieff. 1991. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology 181:595-608. (Erratum, 185: 946.) - PubMed
-
- Bourillot, P. Y., L. Waltzer, A. Sergeant, and E. Manet. 1998. Transcriptional repression by the Epstein-Barr virus EBNA3A protein tethered to DNA does not require RBP-Jkappa. J. Gen. Virol. 79:363-370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

