Actin- and myosin-driven movement of viruses along filopodia precedes their entry into cells
- PMID: 16027225
- PMCID: PMC2171413
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200503059
Actin- and myosin-driven movement of viruses along filopodia precedes their entry into cells
Abstract
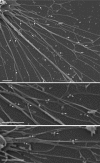
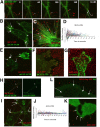
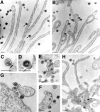
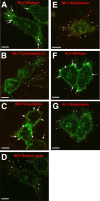
Viruses have often been observed in association with the dense microvilli of polarized epithelia as well as the filopodia of nonpolarized cells, yet whether interactions with these structures contribute to infection has remained unknown. Here we show that virus binding to filopodia induces a rapid and highly ordered lateral movement, "surfing" toward the cell body before cell entry. Virus cell surfing along filopodia is mediated by the underlying actin cytoskeleton and depends on functional myosin II. Any disruption of virus cell surfing significantly reduces viral infection. Our results reveal another example of viruses hijacking host machineries for efficient infection by using the inherent ability of filopodia to transport ligands to the cell body.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two distinct actin networks drive the protrusion of migrating cells.Science. 2004 Sep 17;305(5691):1782-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1100533. Science. 2004. PMID: 15375270
-
A novel form of motility in filopodia revealed by imaging myosin-X at the single-molecule level.Curr Biol. 2009 Jun 9;19(11):967-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.03.067. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19398338 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging efficient viral infection.Nat Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;9(3):243-4. doi: 10.1038/ncb0307-243. Nat Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17330113 No abstract available.
-
An updated look at actin dynamics in filopodia.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015 Feb;72(2):71-9. doi: 10.1002/cm.21216. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015. PMID: 25786787 Review.
-
The many roles of myosins in filopodia, microvilli and stereocilia.Curr Biol. 2021 May 24;31(10):R586-R602. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.04.005. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34033792 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Legume lectins inhibit human parainfluenza virus type 2 infection by interfering with the entry.Viruses. 2012 Jul;4(7):1104-15. doi: 10.3390/v4071104. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 22852043 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Gag associates with specific uropod-directed microdomains in a manner dependent on its MA highly basic region.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(11):6441-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00040-13. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23536680 Free PMC article.
-
The exosome journey: from biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Apr 23;19(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00730-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33892745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cell biology of HIV-1 and other retroviruses.Retrovirology. 2006 Nov 3;3:77. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-3-77. Retrovirology. 2006. PMID: 17083721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA interference and single particle tracking analysis of hepatitis C virus endocytosis.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Dec;5(12):e1000702. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000702. Epub 2009 Dec 24. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 20041214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abercrombie, M., J.E. Heaysman, and S.M. Pegrum. 1970. The locomotion of fibroblasts in culture. 3. Movements of particles on the dorsal surface of the leading lamella. Exp. Cell Res. 62:389–398. - PubMed
-
- Albritton, L.M., L. Tseng, D. Scadden, and J.M. Cunningham. 1989. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 57:659–666. - PubMed
-
- Bates, P., J.A. Young, and H.E. Varmus. 1993. A receptor for subgroup A Rous sarcoma virus is related to the low density lipoprotein receptor. Cell. 74:1043–1051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

