Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II C-terminus interacts with c-Src: implication for a role in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 16002577
- PMCID: PMC2715351
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0103OC
Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II C-terminus interacts with c-Src: implication for a role in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
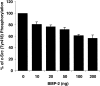
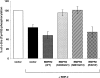
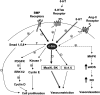
Mutations of bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II (BMPR-II) have been associated with familial and idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). BMPR-II is a member of the transforming growth factor-beta receptor superfamily. It consists of extracellular, transmembrane, and kinase domains, and a unique C-terminus with mostly unknown function. However, a number of PAH-causing mutations are predicted to truncate the C-terminus, suggesting that this domain plays an important role in the homeostasis of pulmonary vessels. In this study, we sought to elucidate the functional role of this C-terminus by seeking its interacting partners. Using yeast two-hybrid screening, we identified c-Src tyrosine kinase as a binding partner of this C-terminus. In vitro co-immunoprecipitation confirmed their interaction. Mutations truncating the C-terminus disrupted their interaction, while missense mutation within kinase domain reduced their interaction. In addition, BMPR-II and c-Src tyrosine kinase colocalized within intracellular aggregates when overexpressed in HEK293 cells. Moreover, mutations truncating the C-terminus disrupted their colocalization, whereas missense mutation within kinase domain had no effect on their colocalization. Furthermore, BMP ligand stimulation decreased c-Src-activating phosphorylation at Tyrosine 418 in pulmonary smooth muscle cells in both time- and concentration-dependent manners. Mutations that truncated the C-terminus abolished this response. Taken together, these results suggest a model in which proliferative effect of c-Src by vasoactive molecules is balanced by opposing effect of BMP signaling in basal state, and the loss of this balance due to BMPR2 mutations leads to increased c-Src activity and subsequently cell growth.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of the bone morphogenetic protein system in endothelin- and aldosterone-induced cell proliferation of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells isolated from human patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Hypertens Res. 2010 May;33(5):435-45. doi: 10.1038/hr.2010.16. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Hypertens Res. 2010. PMID: 20186146
-
Receptor for activated C-kinase 1, a novel interaction partner of type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor, regulates smooth muscle cell proliferation in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Circulation. 2007 Jun 12;115(23):2957-68. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.670026. Epub 2007 May 21. Circulation. 2007. PMID: 17515463
-
Mutations in bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor cause dysregulation of Id gene expression in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells: implications for familial pulmonary arterial hypertension.Circ Res. 2008 May 23;102(10):1212-21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.173567. Epub 2008 Apr 24. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18436795
-
Pulmonary hypertension due to BMPR2 mutation: a new paradigm for tissue remodeling?Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006 Nov;3(8):680-6. doi: 10.1513/pats.200605-118SF. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006. PMID: 17065373 Review.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor mutations causing protein misfolding in heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010 Nov;7(6):395-8. doi: 10.1513/pats.201002-024AW. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010. PMID: 21030519 Review.
Cited by
-
Cadherin-6B is required for the generation of Islet-1-expressing dorsal interneurons.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Apr 10;459(3):504-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.02.136. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 25747715 Free PMC article.
-
Physiologic and molecular consequences of endothelial Bmpr2 mutation.Respir Res. 2011 Jun 22;12(1):84. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-84. Respir Res. 2011. PMID: 21696628 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of rhBMP-2 on pulmonary arterioles remodeling in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats.Clin Exp Med. 2013 Aug;13(3):187-92. doi: 10.1007/s10238-012-0197-2. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Clin Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 22743650
-
Anti-inflammatory and antiatherogenic role of BMP receptor II in endothelial cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Jun;33(6):1350-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300287. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23559633 Free PMC article.
-
BMP2 rescues deficient cell migration in Tgfbr3(-/-) epicardial cells and requires Src kinase.Cell Adh Migr. 2016 May 3;10(3):259-68. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2015.1119362. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Cell Adh Migr. 2016. PMID: 26645362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell 2003;113:685–700. - PubMed
-
- Beppu H, Kawabata M, Hamamoto T, Chytil A, Minowa O, Noda T, Miyazono K. BMP type II receptor is required for gastrulation and early development of mouse embryos. Dev Biol 2000;221:249–258. - PubMed
-
- Delot EC, Bahamonde ME, Zhao M, Lyons KM. BMP signaling is required for septation of the outflow tract of the mammalian heart. Development 2003;130:209–220. - PubMed
-
- Kawabata M, Chytil A, Moses HL. Cloning of a novel type II serine/threonine kinase receptor through interaction with the type I transforming growth factor-beta receptor. J Biol Chem 1995;270:5625–5630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

