Adenovirus E4orf6 targets pp32/LANP to control the fate of ARE-containing mRNAs by perturbing the CRM1-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 15983058
- PMCID: PMC2171388
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200405112
Adenovirus E4orf6 targets pp32/LANP to control the fate of ARE-containing mRNAs by perturbing the CRM1-dependent mechanism
Abstract
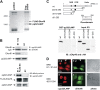
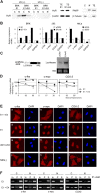
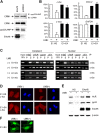
E4orf6 plays an important role in the transportation of cellular and viral mRNAs and is known as an oncogene product of adenovirus. Here, we show that E4orf6 interacts with pp32/leucine-rich acidic nuclear protein (LANP). E4orf6 exports pp32/LANP from the nucleus to the cytoplasm with its binding partner, HuR, which binds to an AU-rich element (ARE) present within many protooncogene and cytokine mRNAs. We found that ARE-mRNAs, such as c-fos, c-myc, and cyclooxygenase-2, were also exported to and stabilized in the cytoplasm of E4orf6-expressing cells. The oncodomain of E4orf6 was necessary for both binding to pp32/LANP and effect for ARE-mRNA. C-fos mRNA was exported together with E4orf6, E1B-55kD, pp32/LANP, and HuR proteins. Moreover, inhibition of the CRM1-dependent export pathway failed to block the export of ARE-mRNAs mediated by E4orf6. Thus, E4orf6 interacts with pp32/LANP to modulate the fate of ARE-mRNAs by altering the CRM1-dependent export pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The adenovirus type 5 E1B-55K oncoprotein actively shuttles in virus-infected cells, whereas transport of E4orf6 is mediated by a CRM1-independent mechanism.J Virol. 2001 Jun;75(12):5677-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.12.5677-5683.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11356976 Free PMC article.
-
Delineation of mRNA export pathways by the use of cell-permeable peptides.Science. 2001 Nov 30;294(5548):1895-901. doi: 10.1126/science.1064693. Science. 2001. PMID: 11729309
-
The adenovirus type 5 E1B-55K oncoprotein is a highly active shuttle protein and shuttling is independent of E4orf6, p53 and Mdm2.Oncogene. 2000 Feb 17;19(7):850-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203395. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10702793
-
Nuclear export of adenovirus RNA.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;259:25-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56597-7_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11417126 Review. No abstract available.
-
mRNA export and cancer.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012 Jan-Feb;3(1):13-25. doi: 10.1002/wrna.101. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012. PMID: 21796793 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Control by DNA Tumor Virus-Encoded Proteins.Pathogens. 2021 May 6;10(5):560. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10050560. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34066504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human antigen R knockdown attenuates the invasive activity of oral cancer cells through inactivation of matrix metalloproteinase-1 gene expression.J Dent Sci. 2024 Jan;19(1):154-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2023.05.014. Epub 2023 May 25. J Dent Sci. 2024. PMID: 38303892 Free PMC article.
-
Conditionally Replicative Adenovirus Controlled by the Stabilization System of AU-Rich Elements Containing mRNA.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 11;12(5):1205. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051205. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32403262 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and characterization of the Anp32e-deficient mouse.PLoS One. 2010 Oct 26;5(10):e13597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013597. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21049064 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Subversion of the Chromosome Region Maintenance 1 Export Pathway and Its Consequences for the Cell Host.Viruses. 2023 Nov 6;15(11):2218. doi: 10.3390/v15112218. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38005895 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aoyagi, M., F. Higashino, M. Yasuda, A. Takahashi, Y. Sawada, Y. Totsuka, T. Kohgo, H. Sano, M. Kobayashi, and M. Shindoh. 2003. Nuclear export of the adenovirus E4orf6 protein is necessary for its ability to antagonize the apoptotic activity of the BH3-only proteins. Oncogene. 22:6919–6927. - PubMed
-
- Campos, A.R., D. Grossman, and K. White. 1985. Mutant alleles at the locus elav in Drosophila melanogaster lead to nervous system defects. A developmental-genetic analysis. J. Neurogenet. 2:197–218. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C.Y., and A.B. Shyu. 1995. AU-rich elements: characterization and importance in mRNA degradation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 20:465–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

