AMOD: a morpholino oligonucleotide selection tool
- PMID: 15980523
- PMCID: PMC1160214
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki453
AMOD: a morpholino oligonucleotide selection tool
Abstract
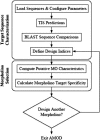
AMOD is a web-based program that aids in the functional evaluation of nucleotide sequences through sequence characterization and antisense morpholino oligonucleotide (target site) selection. Submitted sequences are analyzed by translation initiation site prediction algorithms and sequence-to-sequence comparisons; results are used to characterize sequence features required for morpholino design. Within a defined subsequence, base composition and homodimerization values are computed for all putative morpholino oligonucleotides. Using these properties, morpholino candidates are selected and compared with genomic and transcriptome databases with the goal to identify target-specific enriched morpholinos. AMOD has been used at the University of Minnesota to design approximately 200 morpholinos for a functional genomics screen in zebrafish. The AMOD web server and a tutorial are freely available to both academic and commercial users at http://www.secretomes.umn.edu/AMOD/.
Figures

Similar articles
-
OligoMatcher: analysis and selection of specific oligonucleotide sequences for gene silencing by antisense or siRNA.Appl Bioinformatics. 2006;5(2):121-4. doi: 10.2165/00822942-200605020-00008. Appl Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16722778
-
PriFi: using a multiple alignment of related sequences to find primers for amplification of homologs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jul 1;33(Web Server issue):W516-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki425. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15980525 Free PMC article.
-
TargetFinder: a software for antisense oligonucleotide target site selection based on MAST and secondary structures of target mRNA.Bioinformatics. 2005 Apr 15;21(8):1401-2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti211. Epub 2004 Dec 14. Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15598838
-
Genome-scale probe and primer design with PRIMEGENS.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;402:159-76. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-528-2_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17951795 Review.
-
Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers: favorable properties for sequence-specific gene inactivation.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2001 Jun;3(3):235-8. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2001. PMID: 11497346 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA mimics for the rapid identification of microorganisms by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH).Int J Mol Sci. 2008 Oct;9(10):1944-60. doi: 10.3390/ijms9101944. Epub 2008 Oct 20. Int J Mol Sci. 2008. PMID: 19325728 Free PMC article.
-
Defining synphenotype groups in Xenopus tropicalis by use of antisense morpholino oligonucleotides.PLoS Genet. 2006 Nov 17;2(11):e193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020193. Epub 2006 Oct 4. PLoS Genet. 2006. PMID: 17112317 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide loss-of-function analysis of deubiquitylating enzymes for zebrafish development.BMC Genomics. 2009 Dec 30;10:637. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-637. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 20040115 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide reverse genetics framework to identify novel functions of the vertebrate secretome.PLoS One. 2006 Dec 20;1(1):e104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000104. PLoS One. 2006. PMID: 17218990 Free PMC article.
-
Have we achieved a unified model of photoreceptor cell fate specification in vertebrates?Brain Res. 2008 Feb 4;1192:134-50. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.03.044. Epub 2007 Mar 20. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 17466954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kos R., Reedy M.V., Johnson R.L., Erickson C.A. The wingedhelix transcription factor FoxD3 is important for establishing the neural crest lineage and repressing melanogenesis in avian embryos. Development. 2001;128:1467–1479. - PubMed
-
- Boonanuntanasarn S., Yoshizaki G., Takeuchi Y., Morita T., Takeuchi T. Gene knock-down in rainbow trout embryos using antisense morpholino phosphorodiamidate oligonucleotides. Mar. Biotechnol. 2002;4:256–266. - PubMed
-
- Nasevicius A., Ekker S.C. Effective targeted gene ‘knockdown’ in zebrafish. Nature Genet. 2000;26:216–220. - PubMed
-
- Mellitzer G., Hallonet M., Chen L., Ang S.L. Spatial and temporal ‘knock down’ of gene expression by electroporation of double-stranded RNA and morpholinos into early postimplantation mouse embryos. Mech. Dev. 2002;118:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Yamada L., Shoguchi E., Wada S., Kobayashi K., Mochizuki Y., Satou Y., Satoh N. Morpholino-based gene knockdown screen of novel genes with developmental function in Ciona intestinalis. Development. 2003;130:6485–6495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

