High level expression of apoptosis inhibitor in hepatoma cell line expressing Hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 15968337
- PMCID: PMC1142222
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.2.30
High level expression of apoptosis inhibitor in hepatoma cell line expressing Hepatitis B virus
Abstract
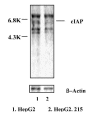
The serious result of hepatitis B (HBV) virus infection is development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the reason of development of HCC in HBV infected patients is still unclear. Recently, the suppression of cell apoptosis is found to relate with the development of cell carcinogenesis, therefore, the expression of apoptosis inhibitor in the virus related cancer line such as hepatoma cell line HepG2.215 was investigated. There are at least six Human apoptosis inhibitors (IAP) have been identified now. They are cIAP1, cIAP2, XIAP, NAPI, survivin and pIAP. Using gene-assay technology, we have recently compared the expression of IAPs in the HepG2.215 cells that persistently expresses Hepatitis B virus by integrated HBV genome with its parent cell line HepG2. The results suggest that there was obviously increase of cIAP2 and cIAP1 in the HepG2.215 cells versus HepG2 cells. Those observations imply a possibility of long time HBV infection could induce the over-expressing apoptosis inhibitors, furthermore, causing the liver cancer. The high expression of cIAP1 and cIAP2 in HBV expressing cells was confirmed by RT-PCR and Northern blot analysis. However, we did not find the change of NIAP and suvivin in HepG2.215 cells. In contrast, the expression of XIAP was down in the HepG2.215 cells comparing with HepG2 cells. How HBV triggers the over-expression of apoptosis inhibitor is unclear. Transient transfection of HepG2 cells with the plasmids expressing different HBV proteins such as S, M, L, X and core proteins did not give a decisive conclusion. Further study is going on now.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

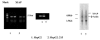
Similar articles
-
The mechanism of apoliprotein A1 down-regulated by Hepatitis B virus.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Mar 25;15:64. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0232-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27015844 Free PMC article.
-
A novel SMAC mimetic APG-1387 exhibits dual antitumor effect on HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma with high expression of cIAP2 by inducing apoptosis and enhancing innate anti-tumor immunity.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;154:127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.04.020. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29679556
-
MiR-19a, miR-122 and miR-223 are differentially regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein and involve in cell proliferation in hepatoma cells.J Transl Med. 2016 May 5;14(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0888-7. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27150195 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting effect of hepatitis B virus on the expressoin of phospholipase A2 group IIA.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Jan 11;16(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0400-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28077172 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins as therapeutic targets in bladder cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 10;13:1124600. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1124600. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36845731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of AMPK/MnSOD signaling mediates anti-apoptotic effect of hepatitis B virus in hepatoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 May 7;22(17):4345-53. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i17.4345. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27158203 Free PMC article.
-
Necroptotic Cell Death in Liver Transplantation and Underlying Diseases: Mechanisms and Clinical Perspective.Liver Transpl. 2019 Jul;25(7):1091-1104. doi: 10.1002/lt.25488. Liver Transpl. 2019. PMID: 31077562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smac mimetic SM-164 potentiates APO2L/TRAIL- and doxorubicin-mediated anticancer activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51461. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051461. Epub 2012 Dec 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23240027 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein accelerates hepatocarcinogenesis with partner survivin through modulating miR-520b and HBXIP.Mol Cancer. 2014 May 28;13:128. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-128. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24886421 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma: consensus recommendations of the National Cancer Institute Clinical Trials Planning Meeting.J Clin Oncol. 2010 Sep 1;28(25):3994-4005. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.28.7805. Epub 2010 Aug 2. J Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20679622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat. Med. 1997;3:917–921. - PubMed
-
- Antoku K, Liu Z, Johnson DE. Inhibition of caspase proteases by CrmA enhances the resistance of human leukemic cells to multiple chemotherapeutic agents. Leukemia. 1997;11(10):1665–72. - PubMed
-
- Beasley RP. The Hepatitis B virus: The major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1988;61:1942–1956. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

