Large-scale profiling of Rab GTPase trafficking networks: the membrome
- PMID: 15944222
- PMCID: PMC1182321
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-01-0062
Large-scale profiling of Rab GTPase trafficking networks: the membrome
Abstract
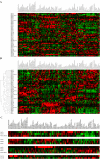
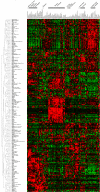
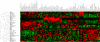
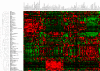
Rab GTPases and SNARE fusion proteins direct cargo trafficking through the exocytic and endocytic pathways of eukaryotic cells. We have used steady state mRNA expression profiling and computational hierarchical clustering methods to generate a global overview of the distribution of Rabs, SNAREs, and coat machinery components, as well as their respective adaptors, effectors, and regulators in 79 human and 61 mouse nonredundant tissues. We now show that this systems biology approach can be used to define building blocks for membrane trafficking based on Rab-centric protein activity hubs. These Rab-regulated hubs provide a framework for an integrated coding system, the membrome network, which regulates the dynamics of the specialized membrane architecture of differentiated cells. The distribution of Rab-regulated hubs illustrates a number of facets that guides the overall organization of subcellular compartments of cells and tissues through the activity of dynamic protein interaction networks. An interactive website for exploring datasets comprising components of the Rab-regulated hubs that define the membrome of different cell and organ systems in both human and mouse is available at http://www.membrome.org/.
Figures
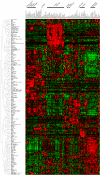
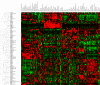
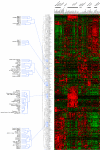
Similar articles
-
Exploring trafficking GTPase function by mRNA expression profiling: use of the SymAtlas web-application and the Membrome datasets.Methods Enzymol. 2005;403:1-10. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)03001-6. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16473572
-
An evolutionary perspective on eukaryotic membrane trafficking.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;607:73-83. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74021-8_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17977460 Review.
-
Rab GTPases: master regulators that establish the secretory and endocytic pathways.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Mar 15;28(6):712-715. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-10-0737. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28292916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rab proteins: the key regulators of intracellular vesicle transport.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Oct 15;328(1):1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.07.027. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 25088255 Review.
-
Rab-mediated vesicle trafficking in cancer.J Biomed Sci. 2016 Oct 6;23(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12929-016-0287-7. J Biomed Sci. 2016. PMID: 27716280 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic functional analysis of rab GTPases reveals limits of neuronal robustness to environmental challenges in flies.Elife. 2021 Mar 5;10:e59594. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59594. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33666175 Free PMC article.
-
Untangling the evolution of Rab G proteins: implications of a comprehensive genomic analysis.BMC Biol. 2012 Aug 8;10:71. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-10-71. BMC Biol. 2012. PMID: 22873208 Free PMC article.
-
Transport to late endosomes is required for efficient reovirus infection.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(16):8346-58. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00100-12. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22674975 Free PMC article.
-
BLOC-1 complex deficiency alters the targeting of adaptor protein complex-3 cargoes.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Sep;17(9):4014-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-02-0103. Epub 2006 Jun 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16760431 Free PMC article.
-
Vacuolin-1 potently and reversibly inhibits autophagosome-lysosome fusion by activating RAB5A.Autophagy. 2014;10(11):1895-905. doi: 10.4161/auto.32200. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Autophagy. 2014. PMID: 25483964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdul-Ghani, M., Gougeon, P. Y., Prosser, D. C., Da-Silva, L. F., and Ngsee, J. K. (2001). PRA isoforms are targeted to distinct membrane compartments. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 6225-6233. - PubMed
-
- Allan, B. B., Moyer, B. D., and Balch, W. E. (2000). Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science 289, 444-448. - PubMed
-
- Antonny, B., and Schekman, R. (2001). ER export: public transportation by the COPII coach. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 438-443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

