Host control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is regulated by 5-lipoxygenase-dependent lipoxin production
- PMID: 15931391
- PMCID: PMC1136995
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23949
Host control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is regulated by 5-lipoxygenase-dependent lipoxin production
Abstract
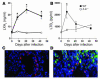
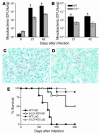
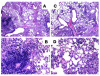
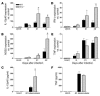
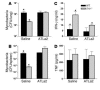
Th1 type cytokine responses are critical in the control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Recent findings indicate that 5-lipoxygenase-dependent (5-LO-dependent) lipoxins regulate host IL-12 production in vivo. Here, we establish lipoxins as key chemical mediators in resistance to M. tuberculosis infection. High levels of lipoxin A4 (LXA4) were detected in sera from infected WT but not infected 5-LO-deficient mice. Moreover, lungs from M. tuberculosis-infected 5-lo-/- animals showed increased IL-12, IFN-gamma, and NO synthase 2 (NOS2) mRNA levels compared with the same tissues in WT mice. Similarly, splenocyte recall responses were enhanced in mycobacteria-infected 5-lo-/- versus WT mice. Importantly, bacterial burdens in 5-lo-/- lungs were significantly lower than those from WT mice, and this enhancement in the resistance of the 5-lo-/- animals to M. tuberculosis was completely prevented by administration of a stable LXA4 analog. Together our results demonstrate that lipoxins negatively regulate protective Th1 responses against mycobacterial infection in vivo and suggest that the inhibition of lipoxin biosynthesis could serve as a strategy for enhancing host resistance to M. tuberculosis.
Figures
Comment in
-
An oily, sustained counter-regulatory response to TB.J Clin Invest. 2005 Jun;115(6):1473-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI25353. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15931386 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
TB: the Yin and Yang of lipid mediators.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;13(4):641-5. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23849093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-Lipoxygenase negatively regulates Th1 response during Brucella abortus infection in mice.Infect Immun. 2015 Mar;83(3):1210-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02592-14. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25583526 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of leukotriene biosynthesis abrogates the host control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Microbes Infect. 2007 Apr;9(4):483-9. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2007.01.006. Epub 2007 Jan 21. Microbes Infect. 2007. PMID: 17347013 Free PMC article.
-
Lower expression of Th1-related cytokines and inducible nitric oxide synthase in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Jan;139(1):57-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02677.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15606614 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity to tuberculosis.Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:599-623. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104635. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15032590 Review.
Cited by
-
TB: the Yin and Yang of lipid mediators.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013 Aug;13(4):641-5. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jul 9. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23849093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-Lipoxygenase activity increases susceptibility to experimental Paracoccidioides brasiliensis infection.Infect Immun. 2013 Apr;81(4):1256-66. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01209-12. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23381993 Free PMC article.
-
The Manipulation of the Lipid Mediator Metabolism as Adjunct Host-Directed Therapy in Tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 12;12:623941. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.623941. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33777003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous lipid mediators in the resolution of airway inflammation.Eur Respir J. 2007 Nov;30(5):980-92. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00005807. Eur Respir J. 2007. PMID: 17978156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foam Cells: One Size Doesn't Fit All.Trends Immunol. 2019 Dec;40(12):1163-1179. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2019.10.002. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Trends Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31732284 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flynn JL, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is required in the protective immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Immunity. 1995;2:561–572. - PubMed
-
- Flynn JL, et al. IL-12 increases resistance of BALB/c mice to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J. Immunol. 1995;155:2515–2524. - PubMed
-
- de Jong R, et al. Severe mycobacterial and Salmonella infections in interleukin-12 receptor-deficient patients. Science. 1998;280:1435–1438. - PubMed
-
- Altare F, et al. Impairment of mycobacterial immunity in human interleukin-12 receptor deficiency. Science. 1998;280:1432–1435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

