EHD proteins associate with syndapin I and II and such interactions play a crucial role in endosomal recycling
- PMID: 15930129
- PMCID: PMC1182304
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-01-0076
EHD proteins associate with syndapin I and II and such interactions play a crucial role in endosomal recycling
Abstract
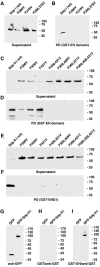
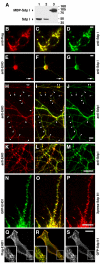
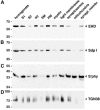
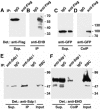
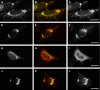
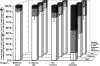
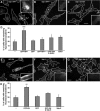
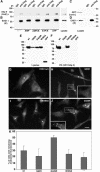
EHD proteins were shown to function in the exit of receptors and other membrane proteins from the endosomal recycling compartment. Here, we identify syndapins, accessory proteins in vesicle formation at the plasma membrane, as differential binding partners for EHD proteins. These complexes are formed by direct eps15-homology (EH) domain/asparagine proline phenylalanine (NPF) motif interactions. Heterologous and endogenous coimmunoprecipitations as well as reconstitutions of syndapin/EHD protein complexes at intracellular membranes of living cells demonstrate the in vivo relevance of the interaction. The combination of mutational analysis and coimmunoprecipitations performed under different nucleotide conditions strongly suggest that nucleotide binding by EHD proteins modulates the association with syndapins. Colocalization studies and subcellular fractionation experiments support a role for syndapin/EHD protein complexes in membrane trafficking. Specific interferences with syndapin-EHD protein interactions by either overexpression of the isolated EHD-binding interface of syndapin II or of the EHD1 EH domain inhibited the recycling of transferrin to the plasma membrane, suggesting that EH domain/NPF interactions are critical for EHD protein function in recycling. Consistently, both inhibitions were rescued by co-overexpression of the attacked protein component. Our data thus reveal that, in addition to a crucial role in endocytic internalization, syndapin protein complexes play an important role in endocytic receptor recycling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complexes of syndapin II with dynamin II promote vesicle formation at the trans-Golgi network.J Cell Sci. 2006 Apr 15;119(Pt 8):1504-16. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02877. Epub 2006 Mar 21. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16551695
-
Interactions between EHD proteins and Rab11-FIP2: a role for EHD3 in early endosomal transport.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Jan;17(1):163-77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-05-0466. Epub 2005 Oct 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16251358 Free PMC article.
-
C-terminal EH-domain-containing proteins: consensus for a role in endocytic trafficking, EH?J Cell Sci. 2005 Sep 15;118(Pt 18):4093-101. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02595. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16155252
-
Molecular remodeling mechanisms of the neural somatodendritic compartment.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Oct;1823(10):1720-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.06.006. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22705351 Review.
-
Mechanisms of EHD/RME-1 protein function in endocytic transport.Traffic. 2008 Dec;9(12):2043-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00834.x. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 18801062 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances and challenges in understanding endosomal sorting and fission.FEBS J. 2023 Sep;290(17):4187-4195. doi: 10.1111/febs.16687. Epub 2022 Dec 7. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 36413090 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of Beclin1 promotes direct cardiac reprogramming.Sci Transl Med. 2020 Oct 21;12(566):eaay7856. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay7856. Sci Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33087505 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of MICAL-L1, syndapin2, and phosphatidic acid in tubular recycling endosome biogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Jun;24(11):1776-90, S1-15. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-01-0026. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23596323 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular physiology of activity-dependent bulk endocytosis of synaptic vesicles.J Neurochem. 2009 Nov;111(4):901-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06384.x. Epub 2009 Sep 16. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19765184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations of EHD1/EHD4 protein levels interfere with L1/NgCAM endocytosis in neurons and disrupt axonal targeting.J Neurosci. 2010 May 12;30(19):6646-57. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5428-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20463227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caplan, S., Naslavsky, N., Hartnell, L. M., Lodge, R., Polishchuk, R. S., Donaldson, J. G., and Bonifacino, J. S. (2002). A tubular EHD1-containing compartment involved in the recycling of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules to the plasma membrane. EMBO J. 21, 2557–2567. - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Beer, T., Hoofnagle, A. N., Enmon, J. L., Bowers, R. C., Yamabhai, M., Kay, B. K., and Overduin, M. (2000). Molecular mechanism of NPF recognition by EH domains. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7, 1018–1022. - PubMed
-
- de Renzis, S., Sonnichsen, B., and Zerial, M. (2002). Divalent Rab effectors regulate the sub-compartmental organization and sorting of early endosomes. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 124–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

