Association of SIGNR1 with TLR4-MD-2 enhances signal transduction by recognition of LPS in gram-negative bacteria
- PMID: 15908446
- PMCID: PMC1343522
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxh264
Association of SIGNR1 with TLR4-MD-2 enhances signal transduction by recognition of LPS in gram-negative bacteria
Abstract
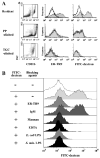
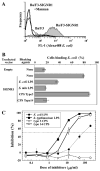
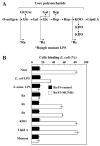
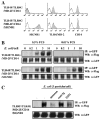
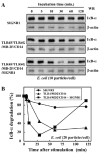
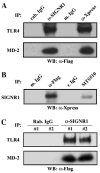
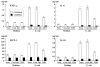
SIGNR1, a member of a new family of mouse C-type lectins, is expressed at high levels in macrophages (Mphi) within the splenic marginal zone, lymph node medulla, and in some strains, in peritoneal cavity. We previously reported that SIGNR1 captures gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, as well as Candida albicans. We have now investigated the precise ligands and innate responses that involve SIGNR1. The interaction of SIGNR1 with FITC-dextran and E. coli was completely inhibited by LPS from E. coli and Salmonella minnesota. Using LPS from various types of rough mutants of Salmonella, we found that SIGNR1 primarily recognizes oligosaccharides in the non-reductive end of the LPS core region. In transfectants, expression of SIGNR1 enhanced the oligomerization of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 molecules as well as the degradation of IkappaB-alpha after stimulation with E. coli under low-serum conditions. The enhanced TLR4 oligomerization was inhibited by pre-treatment of the cells with anti-SIGNR1 mAb or with mannan. A physical association between SIGNR1 and the TLR4-MD-2 complex was also observed by immunoprecipitation. Finally, we found that transfection of SIGNR1 into the macrophage-like RAW264.7 cells resulted in significant augmentation of cytokine production. These results suggest that SIGNR1 associates with TLR4 to capture gram-negative bacteria and facilitate signal transduction to activate innate M responses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acylation determines the toll-like receptor (TLR)-dependent positive versus TLR2-, mannose receptor-, and SIGNR1-independent negative regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines by mycobacterial lipomannan.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 7;282(36):26014-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702690200. Epub 2007 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17617634
-
Efficient capture of Candida albicans and zymosan by SIGNR1 augments TLR2-dependent TNF-α production.Int Immunol. 2012 Feb;24(2):89-96. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxr103. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Int Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22207132
-
C-type lectin SIGNR1 enhances cellular oxidative burst response against C. albicans in cooperation with Dectin-1.Eur J Immunol. 2011 May;41(5):1435-44. doi: 10.1002/eji.200940188. Epub 2011 Mar 14. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21400494
-
Role of Toll-like receptors in inflammatory response in macrophages.Crit Care Med. 2001 Jul;29(7 Suppl):S16-8. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200107001-00008. Crit Care Med. 2001. PMID: 11445728 Review.
-
Sensing Gram-negative bacteria: a phylogenetic perspective.Curr Opin Immunol. 2016 Feb;38:8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.10.007. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26569344 Review.
Cited by
-
Research progress on Toll-like receptor signal transduction and its roles in antimicrobial immune responses.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jul;105(13):5341-5355. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11406-8. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34180006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA stability regulates differential expression of the metastasis protein, osteopontin, in hepatocellular cancer.Surgery. 2008 Jun;143(6):803-12. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2008.02.005. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Surgery. 2008. PMID: 18549897 Free PMC article.
-
DC-SIGN reacts with TLR-4 and regulates inflammatory cytokine expression via NF-κB activation in renal tubular epithelial cells during acute renal injury.Clin Exp Immunol. 2018 Jan;191(1):107-115. doi: 10.1111/cei.13048. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28898406 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the cell biology of the marginal zone of the spleen.Int Rev Cytol. 2006;250:175-215. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(06)50005-1. Int Rev Cytol. 2006. PMID: 16861066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Untangling Cellular Host-Pathogen Encounters at Infection Bottlenecks.Infect Immun. 2023 Apr 18;91(4):e0043822. doi: 10.1128/iai.00438-22. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 36939328 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Figdor CG, van Kooyk Y, Adema GJ. C-type lectin receptors on dendritic cells and Langerhans cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:77. - PubMed
-
- Gallucci S, Matzinger P. Danger signals: SOS to the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol. 2001;13:114. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335. - PubMed
-
- Geijtenbeek TB, Kwon DS, Torensma R, et al. DC-SIGN, a dendritic cell-specific HIV-1-binding protein that enhances trans-infection of T cells. Cell. 2000;100:587. - PubMed
-
- Lozach PY, Lortat-Jacob H, De Lacroix De Lavalette A, et al. DC-SIGN and L-SIGN are high affinity binding receptors for Hepatitis C virus glycoprotein E2. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:20358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

