C --> T mutagenesis and gamma-radiation sensitivity due to deficiency in the Smug1 and Ung DNA glycosylases
- PMID: 15902269
- PMCID: PMC1150883
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600689
C --> T mutagenesis and gamma-radiation sensitivity due to deficiency in the Smug1 and Ung DNA glycosylases
Abstract
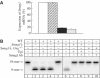
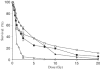
The most common genetic change in aerobic organisms is a C:G to T:A mutation. C --> T transitions can arise through spontaneous hydrolytic deamination of cytosine to give a miscoding uracil residue. This is also a frequent DNA lesion induced by oxidative damage, through exposure to agents such as ionizing radiation, or from endogenous sources that are implicated in the aetiology of degenerative diseases, ageing and cancer. The Ung and Smug1 enzymes excise uracil from DNA to effect repair in mammalian cells, and gene-targeted Ung(-/-) mice exhibit a moderate increase in genome-wide spontaneous mutagenesis. Here, we report that stable siRNA-mediated silencing of Smug1 in mouse embryo fibroblasts also generates a mutator phenotype. However, an additive 10-fold increase in spontaneous C:G to T:A transitions in cells deficient in both Smug1 and Ung demonstrates that these enzymes have distinct and nonredundant roles in suppressing C --> T mutability at non-CpG sites. Such cells are also hypersensitive to ionizing radiation, and reveal a role of Smug1 in the repair of lesions generated by oxidation of cytosine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Uracil Accumulation and Mutagenesis Dominated by Cytosine Deamination in CpG Dinucleotides in Mice Lacking UNG and SMUG1.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 3;7(1):7199. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07314-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28775312 Free PMC article.
-
Uracil-DNA glycosylases SMUG1 and UNG2 coordinate the initial steps of base excision repair by distinct mechanisms.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(12):3879-92. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm372. Epub 2007 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17537817 Free PMC article.
-
Strikingly different properties of uracil-DNA glycosylases UNG2 and SMUG1 may explain divergent roles in processing of genomic uracil.DNA Repair (Amst). 2012 Jun 1;11(6):587-93. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.03.003. Epub 2012 Apr 6. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012. PMID: 22483865
-
Uracil in DNA--general mutagen, but normal intermediate in acquired immunity.DNA Repair (Amst). 2007 Apr 1;6(4):505-16. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.10.014. Epub 2006 Nov 20. DNA Repair (Amst). 2007. PMID: 17116429 Review.
-
Uracil in DNA--occurrence, consequences and repair.Oncogene. 2002 Dec 16;21(58):8935-48. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205996. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12483510 Review.
Cited by
-
Germline ablation of SMUG1 DNA glycosylase causes loss of 5-hydroxymethyluracil- and UNG-backup uracil-excision activities and increases cancer predisposition of Ung-/-Msh2-/- mice.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jul;40(13):6016-25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks259. Epub 2012 Mar 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22447450 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock protein 70 enhanced deoxyribonucleic acid base excision repair in human leukemic cells after ionizing radiation.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2006 Autumn;11(3):240-9. doi: 10.1379/csc-185r.1. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2006. PMID: 17009597 Free PMC article.
-
Lamin A/C promotes DNA base excision repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Dec 16;47(22):11709-11728. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz912. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31647095 Free PMC article.
-
UV-DDB stimulates the activity of SMUG1 during base excision repair of 5-hydroxymethyl-2'-deoxyuridine moieties.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jun 9;51(10):4881-4898. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad206. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36971122 Free PMC article.
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of uracil-processing genes affect the occurrence and the onset of recurrent depressive disorder.PeerJ. 2018 Jun 26;6:e5116. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5116. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 29967751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnes DE, Lindahl T (2004) Repair and genetic consequences of endogenous DNA base damage in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Genet 38: 445–476 - PubMed
-
- Bennett SE, Schimerlik MI, Mosbaugh DW (1993) Kinetics of the uracil-DNA glycosylase/inhibitor protein association. J Biol Chem 268: 26879–26885 - PubMed
-
- Bjelland S, Seeberg E (2003) Mutagenicity, toxicity and repair of DNA base damage induced by oxidation. Mutat Res 531: 37–80 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

