A novel stem-cell population in adult liver with potent hematopoietic-reconstitution activity
- PMID: 15870171
- PMCID: PMC1895213
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-03-1017
A novel stem-cell population in adult liver with potent hematopoietic-reconstitution activity
Abstract
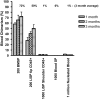
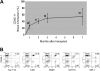
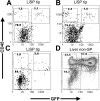
A number of recent reports have documented that cells possessing hematopoietic-reconstitution ability can be identified and isolated from a variety of solid organs in the adult animal. In all studies to date, however, purified organ-derived stem cells demonstrate a diminished repopulating capacity relative to that of purified bone marrow-derived hematopoietic stem cells (BM HSCs). It has therefore been unclear whether organ-derived HSCs possess functional properties distinct from those of BM HSCs, or simply have not been purified to a comparable extent. Here we report the identification of a rare subset of cells in adult murine liver that possess potent blood-repopulating potential, approaching that of BM HSCs. The cells, isolated on the basis of dye-efflux activity and CD45 expression (termed CD45(+) liver side population [SP] tip cells), exhibit a surface phenotype similar to that of freshly isolated BM HSCs derived from normal adult animals, but are phenotypically distinct in that they do not express the stem-cell marker c-kit. Single-cell transplantation studies indicate that CD45(+) liver SP tip cells can be generated from BM HSCs, suggesting a relationship between stem-cell populations in the liver and bone marrow compartments. Overall, these studies have important implications for understanding extramedullary hematopoiesis, and may be relevant to current strategies aimed at inducing tolerance to transplanted organs.
Figures


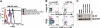
Similar articles
-
Flk-2 is a marker in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation: a simple method to isolate long-term stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Dec 4;98(25):14541-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261562798. Epub 2001 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11724967 Free PMC article.
-
Equal distribution of competitive long-term repopulating stem cells in the CD34+ and CD34- fractions of Thy-1lowLin-/lowSca-1+ bone marrow cells.Exp Hematol. 1998 May;26(5):440-8. Exp Hematol. 1998. PMID: 9590662
-
In vivo differentiation of stem cells in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region of mouse embryo and adult bone marrow.Exp Hematol. 2002 Aug;30(8):957-66. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(02)00822-6. Exp Hematol. 2002. PMID: 12160848
-
Immunophenotype and functional characteristics of human primitive CD34-negative hematopoietic stem cells: the significance of the intra-bone marrow injection.J Autoimmun. 2008 May;30(3):136-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2007.12.004. J Autoimmun. 2008. PMID: 18243660 Review.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell characterization and isolation.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;750:47-59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-145-1_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21618082 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Green fluorescent protein transgene driven by Kit regulatory sequences is expressed in hematopoietic stem cells.Haematologica. 2009 Mar;94(3):318-25. doi: 10.3324/haematol.13689. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Haematologica. 2009. PMID: 19181779 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance and repair of the lung endothelium does not involve contributions from marrow-derived endothelial precursor cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Jul;47(1):11-9. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0180OC. Epub 2012 Feb 9. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22323363 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon gamma inhibits the differentiation of mouse adult liver and bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells by inhibiting the activation of notch signaling.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Jul 16;10(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1311-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31311586 Free PMC article.
-
CD203c is expressed by human fetal hepatoblasts and distinguishes subsets of hepatoblastoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 9;13:927852. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.927852. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36845728 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the lymphopoietic kinetics and features of hematopoietic progenitors contained in the adult murine liver in vivo.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 9;8(10):e76762. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076762. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24130788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spangrude GJ, Heimfeld S, Weissman IL. Purification and characterization of mouse hematopoietic stem cells [published erratum appears in Science. 1989;244:1030]. Science. 1988;241: 58-62. - PubMed
-
- Wright DE, Wagers AJ, Gulati AP, Johnson FL, Weissman IL. Physiological migration of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Science. 2001; 294: 1933-1936. - PubMed
-
- Goodman JW, Hodgson GS. Evidence for stem cells in the peripheral blood of mice. Blood. 1962; 19: 702-714. - PubMed
-
- McKinney-Freeman S, Goodell MA. Circulating hematopoietic stem cells do not efficiently home to bone marrow during homeostasis. Exp Hematol. 2004;32: 868-876. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

