GABAA receptor gamma 2 subunit knockdown mice have enhanced anxiety-like behavior but unaltered hypnotic response to benzodiazepines
- PMID: 15850489
- PMCID: PMC1097738
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-6-30
GABAA receptor gamma 2 subunit knockdown mice have enhanced anxiety-like behavior but unaltered hypnotic response to benzodiazepines
Abstract
Background: Gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors (GABAA-Rs) are the major inhibitory receptors in the mammalian brain and are modulated by a number of sedative/hypnotic drugs including benzodiazepines and anesthetics. The significance of specific GABAA-Rs subunits with respect to behavior and in vivo drug responses is incompletely understood. The gamma2 subunit is highly expressed throughout the brain. Global gamma2 knockout mice are insensitive to the hypnotic effects of diazepam and die perinatally. Heterozygous gamma2 global knockout mice are viable and have increased anxiety-like behaviors. To further investigate the role of the gamma2 subunit in behavior and whole animal drug action, we used gene targeting to create a novel mouse line with attenuated gamma2 expression, i.e., gamma2 knockdown mice.
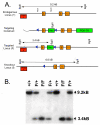
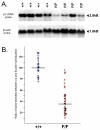
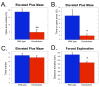
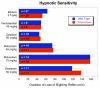
Results: Knockdown mice were created by inserting a neomycin resistance cassette into intron 8 of the gamma2 gene. Knockdown mice, on average, showed a 65% reduction of gamma2 subunit mRNA compared to controls; however gamma2 gene expression was highly variable in these mice, ranging from 10-95% of normal. Immunohistochemical studies demonstrated that gamma2 protein levels were also variably reduced. Pharmacological studies using autoradiography on frozen brain sections demonstrated that binding of the benzodiazepine site ligand Ro15-4513 was decreased in mutant mice compared to controls. Behaviorally, knockdown mice displayed enhanced anxiety-like behaviors on the elevated plus maze and forced novelty exploration tests. Surprisingly, mutant mice had an unaltered response to hypnotic doses of the benzodiazepine site ligands diazepam, midazolam and zolpidem as well as ethanol and pentobarbital. Lastly, we demonstrated that the gamma2 knockdown mouse line can be used to create gamma2 global knockout mice by crossing to a general deleter cre-expressing mouse line.
Conclusion: We conclude that: 1) insertion of a neomycin resistance gene into intron 8 of the gamma2 gene variably reduced the amount of gamma2, and that 2) attenuated expression of gamma2 increased anxiety-like behaviors but did not lead to differences in the hypnotic response to benzodiazepine site ligands. This suggests that reduced synaptic inhibition can lead to a phenotype of increased anxiety-like behavior. In contrast, normal drug effects can be maintained despite a dramatic reduction in GABAA-R targets.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Actions of two GABAA receptor benzodiazepine-site ligands that are mediated via non-γ2-dependent modulation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;666(1-3):111-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 May 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21616065
-
GABA(A) receptor alpha-1 subunit deletion alters receptor subtype assembly, pharmacological and behavioral responses to benzodiazepines and zolpidem.Neuropharmacology. 2002 Sep;43(4):685-94. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00174-0. Neuropharmacology. 2002. PMID: 12367614
-
Amygdala-specific reduction of alpha1-GABAA receptors disrupts the anticonvulsant, locomotor, and sedative, but not anxiolytic, effects of benzodiazepines in mice.J Neurosci. 2010 May 26;30(21):7139-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0693-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20505082 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the mechanism of action of hypnotics.J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13(4 Suppl 1):S11-20. doi: 10.1177/026988119901304S03. J Psychopharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10667451 Review.
-
Analysis of GABAA receptor function and dissection of the pharmacology of benzodiazepines and general anesthetics through mouse genetics.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:475-98. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.44.101802.121429. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004. PMID: 14744255 Review.
Cited by
-
50 years of hurdles and hope in anxiolytic drug discovery.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Sep;12(9):667-87. doi: 10.1038/nrd4075. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23989795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quercetin and/or Ascorbic Acid Modulatory Effect on Phenobarbital-Induced Sleeping Mice Possibly through GABAA and GABAB Receptor Interaction Pathway.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Jul 26;14(8):721. doi: 10.3390/ph14080721. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451819 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of ethanol on behavior and GABAA receptor expression in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) with alternative stress coping styles.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 4;10(1):13076. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69980-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32753576 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in the Alcohol-Mediated Modulation of BLA Network States.eNeuro. 2022 Jul 8;9(4):ENEURO.0010-22.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0010-22.2022. Print 2022 Jul-Aug. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 35788104 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical GABAergic Dysfunction in Stress and Depression: New Insights for Therapeutic Interventions.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Mar 12;13:87. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00087. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30914923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harris RA, Mihic SJ, Brozowski S, Hadingham K, Whiting PJ. Ethanol, flunitrazepam, and pentobarbital modulation of GABAA receptors expressed in mammalian cells and xenopus oocytes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1997;21:444–451. - PubMed
-
- Homanics GE. Gene targeting strategies in the analysis of alcohol and anesthetic mechanisms. In: Accili D, editor. Genetic Manipulation of Receptor Expression and Function. New York, NY , John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2000. pp. 93–110. (Receptor Biochemistry and Methodology). Sibley D., Strader C.
-
- DeBlas AL. Brain GABAa receptors studied with subunit-specific antibodies. Mol Neurobiol. 1996;12:55–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

