Structural implications of novel diversity in eucaryal RNase P RNA
- PMID: 15811915
- PMCID: PMC1370759
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.7211705
Structural implications of novel diversity in eucaryal RNase P RNA
Abstract
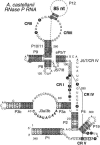
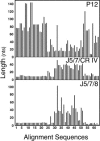
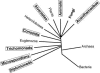
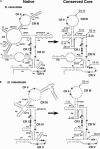
Previous eucaryotic RNase P RNA secondary structural models have been based on limited diversity, representing only two of the approximately 30 phylogenetic kingdoms of the domain Eucarya. To elucidate a more generally applicable structure, we used biochemical, bioinformatic, and molecular approaches to obtain RNase P RNA sequences from diverse organisms including representatives of six additional kingdoms of eucaryotes. Novel sequences were from acanthamoeba (Acathamoeba castellanii, Balamuthia mandrillaris, Filamoeba nolandi), animals (Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster), alveolates (Theileria annulata, Babesia bovis), conosids (Dictyostelium discoideum, Physarum polycephalum), trichomonads (Trichomonas vaginalis), microsporidia (Encephalitozoon cuniculi), and diplomonads (Giardia intestinalis). An improved alignment of eucaryal RNase P RNA sequences was assembled and used for statistical and comparative structural analysis. The analysis identifies a conserved core structure of eucaryal RNase P RNA that has been maintained throughout evolution and indicates that covariation in size occurs between some structural elements of the RNA. Eucaryal RNase P RNA contains regions of highly variable length and structure reminiscent of expansion segments found in rRNA. The eucaryal RNA has been remodeled through evolution as a simplified version of the structure found in bacterial and archaeal RNase P RNAs.
Figures
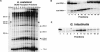

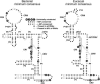
Similar articles
-
Phylogenetic-comparative analysis of the eukaryal ribonuclease P RNA.RNA. 2000 Dec;6(12):1895-904. doi: 10.1017/s1355838200001461. RNA. 2000. PMID: 11142387 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative structure analysis of vertebrate ribonuclease P RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Jul 15;26(14):3333-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.14.3333. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998. PMID: 9649615 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonuclease P: unity and diversity in a tRNA processing ribozyme.Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:153-80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.153. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9759486 Review.
-
Sequence analysis of RNase MRP RNA reveals its origination from eukaryotic RNase P RNA.RNA. 2006 May;12(5):699-706. doi: 10.1261/rna.2284906. Epub 2006 Mar 15. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16540690 Free PMC article.
-
RNase P: interface of the RNA and protein worlds.Trends Biochem Sci. 2006 Jun;31(6):333-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.04.007. Epub 2006 May 6. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006. PMID: 16679018 Review.
Cited by
-
Piece by piece: Building a ribozyme.J Biol Chem. 2020 Feb 21;295(8):2313-2323. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV119.009929. Epub 2020 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31953324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High throughput genome-wide survey of small RNAs from the parasitic protists Giardia intestinalis and Trichomonas vaginalis.Genome Biol Evol. 2009 Jul 6;1:165-75. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evp017. Genome Biol Evol. 2009. PMID: 20333187 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Layers of Stress-Induced Regulation in tRNA Biology.Life (Basel). 2016 Mar 23;6(2):16. doi: 10.3390/life6020016. Life (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27023616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of conserved secondary structures and expansion segments in enod40 RNAs reveals new enod40 homologues in plants.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(9):3144-52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm173. Epub 2007 Apr 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17452360 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of eukaryotic Ribonuclease P RNA.Mol Cell. 2006 Nov 3;24(3):445-56. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.09.011. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 17081993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akmaev, V.R., Kelley, S.T., and Stormo, G.D. 2000. Phylogenetically enhanced statistical tools for RNA structure prediction. Bioinformatics 16: 501–512. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S.F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E.W., and Lipman, D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410. - PubMed
-
- Amaral Zettler, L.A., Nerad, T.A., O’Kelly, C.J., Peglar, M.T., Gillevet, P.M., Silberman, J.D., and Sogin, M.L. 2000. A molecular reassessment of the Leptomyxid amoebae. Protist 151: 275–282. - PubMed
-
- Baldauf, S.L., Roger, A.J., Wenk-Siefert, I., and Doolittle, W.F. 2000. A kingdom-level phylogeny of eukaryotes based on combined protein data. Science 290: 972–977. - PubMed
-
- Ban, N., Nissen, P., Hansen, J., Moore, P.B., and Steitz, T.A. 2000. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science 289: 905–920. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
