MAPPER: a search engine for the computational identification of putative transcription factor binding sites in multiple genomes
- PMID: 15799782
- PMCID: PMC1131891
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-79
MAPPER: a search engine for the computational identification of putative transcription factor binding sites in multiple genomes
Abstract
Background: Cis-regulatory modules are combinations of regulatory elements occurring in close proximity to each other that control the spatial and temporal expression of genes. The ability to identify them in a genome-wide manner depends on the availability of accurate models and of search methods able to detect putative regulatory elements with enhanced sensitivity and specificity.
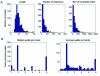
Results: We describe the implementation of a search method for putative transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) based on hidden Markov models built from alignments of known sites. We built 1,079 models of TFBSs using experimentally determined sequence alignments of sites provided by the TRANSFAC and JASPAR databases and used them to scan sequences of the human, mouse, fly, worm and yeast genomes. In several cases tested the method identified correctly experimentally characterized sites, with better specificity and sensitivity than other similar computational methods. Moreover, a large-scale comparison using synthetic data showed that in the majority of cases our method performed significantly better than a nucleotide weight matrix-based method.
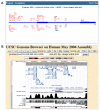
Conclusion: The search engine, available at http://mapper.chip.org, allows the identification, visualization and selection of putative TFBSs occurring in the promoter or other regions of a gene from the human, mouse, fly, worm and yeast genomes. In addition it allows the user to upload a sequence to query and to build a model by supplying a multiple sequence alignment of binding sites for a transcription factor of interest. Due to its extensive database of models, powerful search engine and flexible interface, MAPPER represents an effective resource for the large-scale computational analysis of transcriptional regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The MAPPER database: a multi-genome catalog of putative transcription factor binding sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 1;33(Database issue):D91-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki103. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15608292 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide prediction of transcriptional regulatory elements of human promoters using gene expression and promoter analysis data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Jul 4;7:330. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-330. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16817975 Free PMC article.
-
CREME: Cis-Regulatory Module Explorer for the human genome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jul 1;32(Web Server issue):W253-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh385. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15215390 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of altered cis-regulatory elements in human disease.Trends Genet. 2015 Feb;31(2):67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.12.003. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Trends Genet. 2015. PMID: 25637093 Review.
-
Locating mammalian transcription factor binding sites: a survey of computational and experimental techniques.Genome Res. 2006 Dec;16(12):1455-64. doi: 10.1101/gr.4140006. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 17053094 Review.
Cited by
-
Isoform diversity and its importance for axon regeneration.Neuropathology. 2012 Aug;32(4):420-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2011.01280.x. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Neuropathology. 2012. PMID: 22151581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAM17_i33708A>G polymorphism interacts with dietary n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids to modulate obesity risk in the Genetics of Lipid Lowering Drugs and Diet Network study.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010 Dec;20(10):698-705. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2009.06.011. Epub 2009 Oct 9. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010. PMID: 19819120 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of ABCG5/G8 polymorphisms on HDL-cholesterol concentrations depend on ABCA1 genetic variants in the Boston Puerto Rican Health Study.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010 Oct;20(8):558-66. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2009.05.005. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010. PMID: 19692220 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of human CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 genes and their shared bidirectional promoter in eight world populations.Hum Mutat. 2010 Jan;31(1):27-40. doi: 10.1002/humu.21132. Hum Mutat. 2010. PMID: 19802894 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory gene regulatory networks in amnion cells following cytokine stimulation: translational systems approach to modeling human parturition.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020560. Epub 2011 Jun 2. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21655103 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

