Host and viral proteins in the virion of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
- PMID: 15795281
- PMCID: PMC1069574
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.8.4952-4964.2005
Host and viral proteins in the virion of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
Abstract
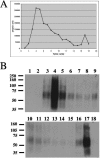
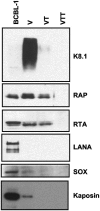
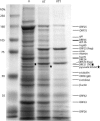
Infection of cultured cells with Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus (KSHV) typically establishes a latent infection, in which only a few viral genes are expressed. Recently, it has been reported that a subset of lytic genes are transiently expressed very early after viral entry but that this burst of abortive lytic gene expression is terminated with the supervention of latency (H. H. Krishnan, P. P. Naranatt, M. S. Smith, L. Zeng, C. Bloomer, and B. Chandran, J. Virol. 78:3601-3620, 2004). To identify molecules imported into cells by KSHV that might influence this gene expression program, we have examined the protein composition of the KSHV particle. Immunoblotting of virus particles demonstrated that RTA, the lytic switch protein, and RAP, a viral protein that is a transcriptional and cell cycle modulator, were both incorporated into virus particles. In a second approach, polypeptides isolated from purified virions were identified by mass-spectrometric analysis of their constituent tryptic peptides. With this approach we were able to identify 18 major virion proteins, including structural, regulatory, and signaling proteins of both viral and cellular origin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus during de novo primary infection of human B and endothelial cells.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(6):3093-111. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02507-14. Epub 2014 Dec 31. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25552714 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase 2 induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus early during in vitro infection of target cells plays a role in the maintenance of latent viral gene expression.J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(13):6534-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00231-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16775340 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded latency-associated nuclear antigen inhibits lytic replication by targeting Rta: a potential mechanism for virus-mediated control of latency.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(12):6585-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.12.6585-6594.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15163750 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen by the lytic transactivator RTA: a novel mechanism for establishment of latency.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(12):7453-65. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7453-7465.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15919901 Free PMC article.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus thymidine kinase is a centrosomal resident precisely localized to the periphery of centrioles.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(12):6523-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00147-07. Epub 2007 Apr 11. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17428875 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic identification of dengue virus binding proteins in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes and Aedes albopictus cells.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:875958. doi: 10.1155/2013/875958. Epub 2013 Nov 10. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24324976 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Composition of the Bovine Herpesvirus 1.1 Virion.Vet Sci. 2017 Feb 20;4(1):11. doi: 10.3390/vetsci4010011. Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 29056670 Free PMC article.
-
ORF33 and ORF38 of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Interact and Are Required for Optimal Production of Infectious Progeny Viruses.J Virol. 2015 Dec 4;90(4):1741-56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02738-15. Print 2016 Feb 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26637455 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and unusual small RNAs discovered in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus virions.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(23):12717-30. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01473-12. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22973026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akula, S. M., N. P. Pramod, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2002. Integrin alpha3beta1 (CD 49c/29) is a cellular receptor for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) entry into the target cells. Cell 108:407-419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

