The archaeal eIF2 homologue: functional properties of an ancient translation initiation factor
- PMID: 15788752
- PMCID: PMC1069517
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki321
The archaeal eIF2 homologue: functional properties of an ancient translation initiation factor
Abstract
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2) is pivotal for delivery of the initiator tRNA (tRNAi) to the ribosome. Here, we report the functional characterization of the archaeal homologue, a/eIF2. We have cloned the genes encoding the three subunits of a/eIF2 from the thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus, and have assayed the activities of the purified recombinant proteins in vitro. We demonstrate that the trimeric factor reconstituted from the recombinant polypeptides has properties similar to those of its eukaryal homologue: it interacts with GTP and Met-tRNAi, and stimulates binding of the latter to the small ribosomal subunit. However, the archaeal protein differs in some functional aspects from its eukaryal counterpart. In contrast to eIF2, a/eIF2 has similar affinities for GDP and GTP, and the beta-subunit does not contribute to tRNAi binding. The detailed analysis of the complete trimer and of its isolated subunits is discussed in light of the evolutionary history of the eIF2-like proteins.
Figures

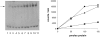
Similar articles
-
New insights into the interactions of the translation initiation factor 2 from archaea with guanine nucleotides and initiator tRNA.J Mol Biol. 2007 Oct 19;373(2):328-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.048. Epub 2007 Aug 2. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17825838
-
Archaeal translation initiation factor aIF2 can substitute for eukaryotic eIF2 in ribosomal scanning during mammalian 48S complex formation.J Mol Biol. 2011 Oct 14;413(1):106-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.08.026. Epub 2011 Aug 23. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21884705
-
Conformational transitions in the γ subunit of the archaeal translation initiation factor 2.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Mar;70(Pt 3):658-67. doi: 10.1107/S1399004713032240. Epub 2014 Feb 15. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 24598735
-
Translation initiation in Archaea: conserved and domain-specific features.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Jan;39(1):89-93. doi: 10.1042/BST0390089. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21265752 Review.
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999 Jan;31(1):25-9. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(98)00128-9. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10216940 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive analysis of the importance of translation initiation factors for Haloferax volcanii applying deletion and conditional depletion mutants.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 14;8(11):e77188. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077188. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244275 Free PMC article.
-
A presumed homologue of the regulatory subunits of eIF2B functions as ribose-1,5-bisphosphate isomerase in Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 30;8(1):1891. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20418-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29382938 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an RNase J ortholog in Sulfolobus solfataricus: implications for 5'-to-3' directional decay and 5'-end protection of mRNA in Crenarchaeota.RNA. 2011 Jan;17(1):99-107. doi: 10.1261/rna.2418211. Epub 2010 Nov 29. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21115637 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of yeast eIF2α and eIF2β subunits in the binding of the initiator methionyl-tRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(2):1047-57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1180. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23193270 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of scanning and start codon selection in eukaryotes.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Sep;75(3):434-67, first page of table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00008-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21885680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gualerzi C.O., Pon C.L. Initiation of mRNA translation in prokaryotes. Biochemistry. 1990;29:5881–5889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

