Human mRNA cap methyltransferase: alternative nuclear localization signal motifs ensure nuclear localization required for viability
- PMID: 15767670
- PMCID: PMC1061643
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.7.2644-2649.2005
Human mRNA cap methyltransferase: alternative nuclear localization signal motifs ensure nuclear localization required for viability
Abstract
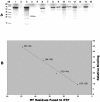
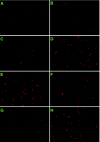
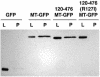
A characteristic feature of gene expression in eukaryotes is the addition of a 5'-terminal 7-methylguanine cap (m7GpppN) to nascent pre-mRNAs in the nucleus catalyzed by capping enzyme and cap methyltransferase. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) knockdown of cap methyltransferase in HeLa cells resulted in apoptosis as measured by terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP-tetramethylrhodamine nick end labeling assay, demonstrating the importance of mRNA 5'-end methylation for mammalian cell viability. Nuclear localization of cap methyltransferase is mediated by interaction with importin-alpha, which facilitates its transport and selective binding to transcripts containing 5'-terminal GpppN. The methyltransferase 96-144 region has been shown to be necessary for importin binding, and N-terminal fusion of this sequence to nonnuclear proteins proved sufficient for nuclear localization. The targeting sequence was narrowed to amino acids 120 to 129, including a required 126KRK. Although full-length methyltransferase (positions 1 to 476) contains the predicted nuclear localization signals 57RKRK, 80KKRK, 103KKRKR, and 194KKKR, mutagenesis studies confirmed functional motifs only at positions 80, 103, and the previously unrecognized 126KRK. All three motifs can act as alternative nu clear targeting signals. Expression of N-truncated cap methyltransferase (120 to 476) restored viability of methyltransferase siRNA knocked-down cells. However, an enzymatically active 144-476 truncation mutant missing the three nuclear localization signals was mostly cytoplasmic and ineffective in preventing siRNA-induced loss of viability.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nuclear transport of Ras-associated tumor suppressor proteins: different transport receptor binding specificities for arginine-rich nuclear targeting signals.J Mol Biol. 2007 Apr 13;367(5):1294-311. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.01.026. Epub 2007 Jan 12. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17320110
-
Identification of nuclear import and export signals within Fli-1: roles of the nuclear import signals in Fli-1-dependent activation of megakaryocyte-specific promoters.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Apr;25(8):3087-108. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.8.3087-3108.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15798196 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear transport of Kir/Gem requires specific signals and importin alpha5 and is regulated by calmodulin and predicted serine phosphorylations.Traffic. 2007 Sep;8(9):1150-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00598.x. Epub 2007 Jul 1. Traffic. 2007. PMID: 17605761
-
Regulation of mRNA capping in the cell cycle.RNA Biol. 2017 Jan 2;14(1):11-14. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1251540. Epub 2016 Oct 28. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27791484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation and function of CMTR1-dependent mRNA cap methylation.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017 Nov;8(6):e1450. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1450. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017. PMID: 28971629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RAM function is dependent on Kapβ2-mediated nuclear entry.Biochem J. 2014 Feb 1;457(3):473-84. doi: 10.1042/BJ20131359. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 24200467 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced mRNA cap methylation increases cyclin D1 expression and promotes cell transformation.Oncogene. 2010 Feb 11;29(6):930-6. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.368. Epub 2009 Nov 16. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 19915615 Free PMC article.
-
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E elevates steady-state m7G capping of coding and noncoding transcripts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Oct 27;117(43):26773-26783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2002360117. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33055213 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of 12 m7G methylation-related miRNA markers and their correlation with immune infiltration in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 5;12:929363. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.929363. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35992830 Free PMC article.
-
CDK1-Cyclin B1 Activates RNMT, Coordinating mRNA Cap Methylation with G1 Phase Transcription.Mol Cell. 2016 Mar 3;61(5):734-746. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.008. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26942677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Furuichi, Y., S. Muthukrishnan, J. Tomasz, and A. J. Shatkin. 1976. Mechanism of formation of reovirus mRNA 5′-terminal blocked and methylated sequence, m7GpppGmpC. J. Biol. Chem. 251:5043-5053. - PubMed
-
- Gingras, A. C., B. Raught, and N. Sonenberg. 1999. eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68:913-963. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
