Myosin-1a is critical for normal brush border structure and composition
- PMID: 15758024
- PMCID: PMC1087248
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1116
Myosin-1a is critical for normal brush border structure and composition
Abstract
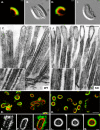
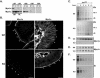
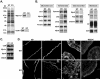
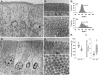
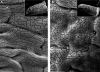
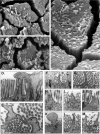
To develop our understanding of myosin-1a function in vivo, we have created a mouse line null for the myosin-1a gene. Myosin-1a knockout mice demonstrate no overt phenotypes at the whole animal level but exhibit significant perturbations and signs of stress at the cellular level. Among these are defects in microvillar membrane morphology, distinct changes in brush-border organization, loss of numerous cytoskeletal and membrane components from the brush border, and redistribution of intermediate filament proteins into the brush border. We also observed significant ectopic recruitment of another short-tailed class I motor, myosin-1c, into the brush border of knockout enterocytes. This latter finding, a clear demonstration of functional redundancy among vertebrate myosins-I, may account for the lack of a whole animal phenotype. Nevertheless, these results indicate that myosin-1a is a critical multifunctional component of the enterocyte, required for maintaining the normal composition and highly ordered structure of the brush border.
Figures




Comment in
-
An MBoC favorite: Myosin-1a is critical for normal brush border structure and composition.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jul;23(13):2401. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0188. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22745338 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Differential localization and dynamics of class I myosins in the enterocyte microvillus.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 15;21(6):970-8. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0638. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20089841 Free PMC article.
-
An MBoC favorite: Myosin-1a is critical for normal brush border structure and composition.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jul;23(13):2401. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0188. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22745338 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Myosin 5b is required for proper localization of the intermicrovillar adhesion complex in the intestinal brush border.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022 Nov 1;323(5):G501-G510. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00212.2022. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36218265 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping the intestinal brush border.J Cell Biol. 2014 Nov 24;207(4):441-51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201407015. J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25422372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid raft organization and function in brush borders of epithelial cells.Mol Membr Biol. 2006 Jan-Feb;23(1):71-9. doi: 10.1080/09687860500445604. Mol Membr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16611582 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between planar cell polarity signaling and miR-8 control of NHERF1-mediated actin reorganization.Cell Cycle. 2010 Jan 15;9(2):235-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.2.10434. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Cell Cycle. 2010. PMID: 20023383 Free PMC article.
-
Differential localization and dynamics of class I myosins in the enterocyte microvillus.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 15;21(6):970-8. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0638. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20089841 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin-1a powers the sliding of apical membrane along microvillar actin bundles.J Cell Biol. 2007 May 21;177(4):671-81. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200701144. Epub 2007 May 14. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17502425 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity in membrane cholesterol contributes toward electrical maturation of hearing.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 18;286(7):5768-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.186486. Epub 2010 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21163952 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin Id is required for planar cell polarity in ciliated tracheal and ependymal epithelial cells.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015 Oct;72(10):503-16. doi: 10.1002/cm.21259. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2015. PMID: 26446290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman, D., Sweeney, H. L., and Spudich, J. A. (2004). The mechanism of myosin VI translocation and its load-induced anchoring. Cell 116, 737-749. - PubMed
-
- Braccia, A., Villani, M., Immerdal, L., Niels-Christiansen, L. L., Nystrom, B. T., Hansen, G. H., and Danielsen, E. M. (2003). Microvillar membrane microdomains exist at physiological temperature. Role of galectin-4 as lipid raft stabilizer revealed by “superrafts.” J. Biol. Chem. 278, 15679-15684. - PubMed
-
- Brown, D. A., and London, E. (1998). Functions of lipid rafts in biological membranes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 14, 111-136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

