Analysis of mouse embryonic patterning and morphogenesis by forward genetics
- PMID: 15755804
- PMCID: PMC1087930
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0501071102
Analysis of mouse embryonic patterning and morphogenesis by forward genetics
Abstract
Many aspects of the genetic control of mammalian embryogenesis cannot be extrapolated from other animals. Taking a forward genetic approach, we have induced recessive mutations by treatment of mice with ethylnitrosourea and have identified 43 mutations that affect early morphogenesis and patterning, including 38 genes that have not been studied previously. The molecular lesions responsible for 14 mutations were identified, including mutations in nine genes that had not been characterized previously. Some mutations affect vertebrate-specific components of conserved signaling pathways; for example, at least five mutations affect previously uncharacterized regulators of the Sonic hedgehog (Shh) pathway. Approximately half of all of the mutations affect the initial establishment of the body plan, and several of these produce phenotypes that have not been described previously. A large fraction of the genes identified affect cell migration, cellular organization, and cell structure. The findings indicate that phenotype-based genetic screens provide a direct and unbiased method to identify essential regulators of mammalian development.
Figures
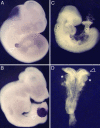

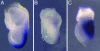

Comment in
-
Biography of Kathryn V. Anderson.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Apr 26;102(17):5910-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501900102. Epub 2005 Apr 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15840717 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Uncovering the uncharacterized and unexpected: unbiased phenotype-driven screens in the mouse.Dev Dyn. 2006 Sep;235(9):2412-23. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20853. Dev Dyn. 2006. PMID: 16724327 Review.
-
A phenotype-based screen for embryonic lethal mutations in the mouse.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jun 23;95(13):7485-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7485. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9636176 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of recessive maternal-effect mutations in the zebrafish using a gynogenesis-based method.Dev Dyn. 2004 Oct;231(2):324-35. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20145. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 15366009
-
Finding the genes that direct mammalian development : ENU mutagenesis in the mouse.Trends Genet. 2000 Mar;16(3):99-102. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(99)01921-6. Trends Genet. 2000. PMID: 10689347 Review.
-
Screening mosaic F1 females for mutations affecting zebrafish heart induction and patterning.Dev Genet. 1998;22(3):288-99. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1998)22:3<288::AID-DVG10>3.0.CO;2-2. Dev Genet. 1998. PMID: 9621435
Cited by
-
A stem cell roadmap of ribosome heterogeneity reveals a function for RPL10A in mesoderm production.Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 19;13(1):5491. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33263-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36123354 Free PMC article.
-
Biography of Kathryn V. Anderson.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Apr 26;102(17):5910-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501900102. Epub 2005 Apr 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15840717 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ttc21b is required to restrict sonic hedgehog activity in the developing mouse forebrain.Dev Biol. 2009 Nov 1;335(1):166-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.08.023. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19732765 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar transport protein 122 antagonizes Sonic Hedgehog signaling and controls ciliary localization of pathway components.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 25;108(4):1456-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1011410108. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21209331 Free PMC article.
-
Chato, a KRAB zinc-finger protein, regulates convergent extension in the mouse embryo.Development. 2008 Sep;135(18):3053-62. doi: 10.1242/dev.022897. Epub 2008 Aug 13. Development. 2008. PMID: 18701545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rossant, J. & Tam, P. P. (2004) Dev. Cell 7, 155-164. - PubMed
-
- Nüsslein-Volhard, C. (1991) Dev. Suppl. 1, 1-10. - PubMed
-
- Bowerman, B. (1998) Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 39, 73-117. - PubMed
-
- Jesuthasan, S. & Strähle, U. (1997) Curr. Biol. 7, 31-42. - PubMed
-
- Rossant, J. & Cross, J. C. (2001) Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 538-548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

