On the role of Cro in lambda prophage induction
- PMID: 15728734
- PMCID: PMC555511
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409839102
On the role of Cro in lambda prophage induction
Abstract
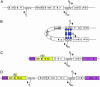
The lysogenic state of bacteriophage lambda is exceptionally stable yet the prophage is readily induced in response to DNA damage. This delicate epigenetic switch is believed to be regulated by two proteins; the lysogenic maintenance promoting protein CI and the early lytic protein Cro. First, we confirm, in the native configuration, the previous observation that the DNA loop mediated by oligomerization of CI bound to two distinct operator regions (O(L) and O(R)), increases repression of the early lytic promoters and is important for stable maintenance of lysogeny. Second, we show that the presence of the cro gene might be unimportant for the lysogenic to lytic switch during induction of the lambda prophage. We revisit the idea that Cro's primary role in induction is instead to mediate weak repression of the early lytic promoters.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of the lytic repressor in prophage induction of phage lambda as analyzed by a module-replacement approach.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Mar 21;103(12):4558-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511117103. Epub 2006 Mar 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16537413 Free PMC article.
-
The Developmental Switch in Bacteriophage λ: A Critical Role of the Cro Protein.J Mol Biol. 2018 Jan 5;430(1):58-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 20. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29158090 Free PMC article.
-
Cro's role in the CI Cro bistable switch is critical for {lambda}'s transition from lysogeny to lytic development.Genes Dev. 2007 Oct 1;21(19):2461-72. doi: 10.1101/gad.1584907. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17908932 Free PMC article.
-
lambda Repressor and cro--components of an efficient molecular switch.Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):217-23. doi: 10.1038/294217a0. Nature. 1981. PMID: 6457992 Review.
-
Yet another way that phage λ manipulates its Escherichia coli host: λrexB is involved in the lysogenic-lytic switch.Mol Microbiol. 2015 May;96(4):689-93. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12969. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25684601 Review.
Cited by
-
Paradigms of pathogenesis: targeting the mobile genetic elements of disease.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Dec 14;2:161. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00161. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23248780 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Transcription is regulated by NusA:NusG interaction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 8;44(12):5971-82. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw423. Epub 2016 May 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27174929 Free PMC article.
-
XRE transcription factors conserved in Caulobacter and φCbK modulate adhesin development and phage production.PLoS Genet. 2023 Nov 16;19(11):e1011048. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011048. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37972151 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal frameshifting and dual-target antiactivation restrict quorum-sensing-activated transfer of a mobile genetic element.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 31;112(13):4104-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1501574112. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25787256 Free PMC article.
-
A quantitative study of lambda-phage SWITCH and its components.Biophys J. 2007 Apr 15;92(8):2685-93. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.106.097089. Epub 2007 Jan 26. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17259278 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

