siRNA target site secondary structure predictions using local stable substructures
- PMID: 15722476
- PMCID: PMC549425
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gni026
siRNA target site secondary structure predictions using local stable substructures
Erratum in
- Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(16):4653
Abstract
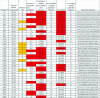
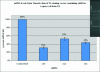
The crystal structure based model of the catalytic center of Ago2 revealed that the siRNA and the mRNA must be able to form an A-helix for correct positing of the scissile phosphate bond for cleavage in RNAi. This suggests that base pairing of the target mRNA with itself, i.e. secondary structure, must be removed before cleavage. Early on in the siRNA design, GC-rich target sites were avoided because of their potential to be involved in strong secondary structure. It is still unclear how important a factor mRNA secondary structure is in RNAi. However, it has been established that a difference in the thermostability of the ends of an siRNA duplex dictate which strand is loaded into the RNA-induced silencing complex. Here, we use a novel secondary structure prediction method and duplex-end differential calculations to investigate the importance of a secondary structure in the siRNA design. We found that the differential duplex-end stabilities alone account for functional prediction of 60% of the 80 siRNA sites examined, and that secondary structure predictions improve the prediction of site efficacy. A total of 80% of the non-functional sites can be eliminated using secondary structure predictions and duplex-end differential.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Local RNA target structure influences siRNA efficacy: systematic analysis of intentionally designed binding regions.J Mol Biol. 2005 May 13;348(4):883-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.011. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15843020
-
Influence of mRNA features on siRNA interference efficacy.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2013 Jun;11(3):1341004. doi: 10.1142/S0219720013410047. Epub 2013 Feb 18. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23796181
-
Silencing efficacy prediction: a retrospective study on target mRNA features.Biosci Rep. 2015 Mar 31;35(2):e00185. doi: 10.1042/BSR20140147. Biosci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25702798 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into mRNA recognition from a PIWI domain-siRNA guide complex.Nature. 2005 Mar 31;434(7033):663-6. doi: 10.1038/nature03462. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15800628 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting siRNA efficiency.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Jul;64(14):1785-92. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7057-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17415516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic siRNA: principles, challenges, and strategies.Yale J Biol Med. 2012 Jun;85(2):187-200. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Yale J Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22737048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An accurate and interpretable model for siRNA efficacy prediction.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Nov 30;7:520. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-520. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17137497 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Secondary Structure Analysis Using RNAstructure.Curr Protoc. 2023 Jul;3(7):e846. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.846. Curr Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37487054 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer-mediated transcriptional gene silencing of Fox p 3 inhibits regulatory T cells and potentiates antitumor response.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 May 8;25:143-151. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.05.005. eCollection 2021 Sep 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34457999 Free PMC article.
-
Design of Potential RNAi (miRNA and siRNA) Molecules for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) Gene Silencing by Computational Method.Interdiscip Sci. 2015 Sep;7(3):257-65. doi: 10.1007/s12539-015-0266-9. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Interdiscip Sci. 2015. PMID: 26223545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elbashir S.M., Harborth J., Weber K., Tuschl T. Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. Methods. 2002;26:199–213. - PubMed
-
- Lingel A., Simon B., Izaurralde E., Sattler M. Nucleic acid 3′-end recognition by the Argonaute2 PAZ domain. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004;11:576–577. - PubMed
-
- Song J.J., Liu J., Tolia N.H., Schneiderman J., Smith S.K., Martienssen R.A., Hannon G.J., Joshua-Tor L. The crystal structure of the Argonaute 2 PAZ domain reveals an RNA binding motif in RNAi effector complexes. Nature Struct. Biol. 2003;10:1026–1032. - PubMed
-
- Lingel A., Simon B., Izaurralde E., Sattler M. Structure and nucleic-acid binding of the Drosophila Argonaute 2 PAZ domain. Nature. 2003;426:465–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

