The structure of an enzyme-activating fragment of human telomerase RNA
- PMID: 15703438
- PMCID: PMC1370729
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.7222505
The structure of an enzyme-activating fragment of human telomerase RNA
Abstract
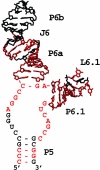
The ribonucleoprotein enzyme telomerase ensures the stability and fidelity of linear chromosome ends by elongating the telomeric DNA that is lost during each round of DNA replication. All telomerases contain a catalytic protein component homologous to viral reverse transcriptases (TERT) and an RNA (TR) that provides the template sequence, acts as the scaffold for ribonucleoprotein assembly, and activates the enzyme for catalysis. Vertebrate telomerase RNAs contain three highly conserved structural and functional domains: the template domain, the "CR4-CR5" or "activation" domain essential for activation of the enzymatic activity, and a 3'-terminal "box H/ACA"-homology domain responsible for ribonucleprotein assembly and maturation. Here we report the NMR structure of a functionally essential RNA structural element derived from the human telomerase RNA CR4-CR5 domain. This RNA, referred to as hTR J6, forms a stable hairpin interrupted by a single nucleotide bulge and an asymmetric internal loop. Previous work on telomerase has shown that deletion of the hTR J6 asymmetric internal loop results in an RNA incapable of binding the enzymatic protein component of the RNP and therefore an inactive RNP without telomerase activity. We demonstrate here that the J6 internal loop introduces a twist in the RNA structure that may position the entire domain into the catalytic site of the enzyme.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The solution structure of an essential stem-loop of human telomerase RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 May 15;31(10):2614-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg351. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12736311 Free PMC article.
-
Human telomerase RNA-protein interactions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Aug 15;29(16):3385-93. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.16.3385. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11504876 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of echinoderm telomerase RNA.RNA. 2016 Feb;22(2):204-15. doi: 10.1261/rna.053280.115. Epub 2015 Nov 23. RNA. 2016. PMID: 26598712 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of telomerase RNA.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006 Jun;16(3):307-18. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.05.005. Epub 2006 May 18. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16713250 Review.
-
Evolutionary perspectives of telomerase RNA structure and function.RNA Biol. 2016 Aug 2;13(8):720-32. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1205768. Epub 2016 Jun 30. RNA Biol. 2016. PMID: 27359343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural analysis of the catalytic core of human telomerase RNA by FRET and molecular modeling.Biochemistry. 2006 Nov 7;45(44):13304-11. doi: 10.1021/bi061150a. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 17073451 Free PMC article.
-
A critical three-way junction is conserved in budding yeast and vertebrate telomerase RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(18):6280-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm713. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17855392 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons learned from a lncRNA odyssey for two genes with vascular functions, DLL4 and TIE1.Vascul Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;114:103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2018.06.010. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30910126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural dynamics of a single-stranded RNA-helix junction using NMR.RNA. 2014 Jun;20(6):782-91. doi: 10.1261/rna.043711.113. Epub 2014 Apr 17. RNA. 2014. PMID: 24742933 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and folding of the Tetrahymena telomerase RNA pseudoknot.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 9;45(1):482-495. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1153. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aboul-ela, F., Karn, J., and Varani, G. 1995. The structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type-1 Tar RNA reveals principles of RNA recognition by Tat protein. J. Mol. Biol. 253: 313–332. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hashimi, H.M., Gosser, Y., Gorin, A., Hu, W., Majumdar, A., and Patel, D.J. 2002. Concerted motions in Hiv-1 Tar RNA may allow access to bound state conformations: RNA dynamics from Nmr residual dipolar couplings. J. Mol. Biol. 315: 95–102. - PubMed
-
- Allain, F.H.-T. and Varani, G. 1995. Structure of the P1 helix from group I self splicing introns. J. Mol. Biol. 250: 333–353. - PubMed
-
- Andersson, P., Weigelt, J., and Otting, G. 1998. Spin-state selection filters for the measurement of heteronuclear one-bond coupling constants. J. Biomol. NMR 12: 435–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
