Ectopic expression of an activated RAC in Arabidopsis disrupts membrane cycling
- PMID: 15703216
- PMCID: PMC1073671
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0562
Ectopic expression of an activated RAC in Arabidopsis disrupts membrane cycling
Abstract
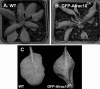
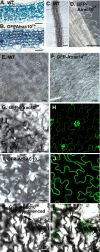
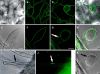
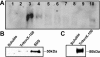
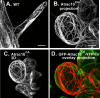
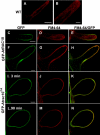
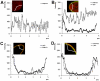
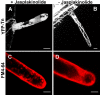
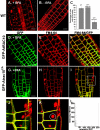
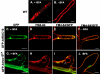
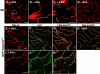
Rho GTPases regulate the actin cytoskeleton, exocytosis, endocytosis, and other signaling cascades. Rhos are subdivided into four subfamilies designated Rho, Racs, Cdc42, and a plant-specific group designated RACs/Rops. This research demonstrates that ectopic expression of a constitutive active Arabidopsis RAC, AtRAC10, disrupts actin cytoskeleton organization and membrane cycling. We created transgenic plants expressing either wild-type or constitutive active AtRAC10 fused to the green fluorescent protein. The activated AtRAC10 induced deformation of root hairs and leaf epidermal cells and was primarily localized in Triton X-100-insoluble fractions of the plasma membrane. Actin cytoskeleton reorganization was revealed by creating double transgenic plants expressing activated AtRAC10 and the actin marker YFP-Talin. Plants were further analyzed by membrane staining with N-[3-triethylammoniumpropyl]-4-[p-diethylaminophenylhexatrienyl] pyridinium dibromide (FM4-64) under different treatments, including the protein trafficking inhibitor brefeldin A or the actin-depolymeryzing agents latrunculin-B (Lat-B) and cytochalasin-D (CD). After drug treatments, activated AtRAC10 did not accumulate in brefeldin A compartments, but rather reduced their number and colocalized with FM4-64-labeled membranes in large intracellular vesicles. Furthermore, endocytosis was compromised in root hairs of activated AtRAC10 transgenic plants. FM4-64 was endocytosed in nontransgenic root hairs treated with the actin-stabilizing drug jasplakinolide. These findings suggest complex regulation of membrane cycling by plant RACs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Novel ROP/RAC effector links cell polarity, root-meristem maintenance, and vesicle trafficking.Curr Biol. 2007 Jun 5;17(11):947-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.04.038. Epub 2007 May 10. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17493810
-
Modification of plant Rac/Rop GTPase signalling using bacterial toxin transgenes.Plant J. 2013 Jan;73(2):314-24. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12040. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Plant J. 2013. PMID: 23020817
-
High expression of Lifeact in Arabidopsis thaliana reduces dynamic reorganization of actin filaments but does not affect plant development.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011 Oct;68(10):578-87. doi: 10.1002/cm.20534. Epub 2011 Oct 4. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 21948789
-
The actin cytoskeleton in root hairs: all is fine at the tip.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2013 Dec;16(6):749-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2013.10.003. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 24446547 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms controlling pavement cell shape in Arabidopsis leaves.Plant Cell Rep. 2009 Aug;28(8):1147-57. doi: 10.1007/s00299-009-0729-8. Epub 2009 Jun 16. Plant Cell Rep. 2009. PMID: 19529941 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of membrane trafficking, cytoskeleton dynamics, and cell polarity by ROP/RAC GTPases.Plant Physiol. 2008 Aug;147(4):1527-43. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.122150. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18678744 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Corrected and Republished from: Activation Status-Coupled Transient S-Acylation Determines Membrane Partitioning of a Plant Rho-Related GTPase.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Nov 13;37(23):e00333-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00333-17. Print 2017 Dec 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28894027 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule-associated ROP interactors affect microtubule dynamics and modulate cell wall patterning and root hair growth.Development. 2022 Nov 15;149(22):dev200811. doi: 10.1242/dev.200811. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Development. 2022. PMID: 36314989 Free PMC article.
-
ROP GTPase-dependent actin microfilaments promote PIN1 polarization by localized inhibition of clathrin-dependent endocytosis.PLoS Biol. 2012;10(4):e1001299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001299. Epub 2012 Apr 3. PLoS Biol. 2012. PMID: 22509133 Free PMC article.
-
A rho scaffold integrates the secretory system with feedback mechanisms in regulation of auxin distribution.PLoS Biol. 2010 Jan 19;8(1):e1000282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000282. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 20098722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrawal, G. K., Iwahashi, H., and Rakwal, R. (2003). Small GTPase `Rop': molecular switch for plant defense responses. FEBS Lett. 546, 173-180. - PubMed
-
- Baluska, F., Hlavacka, A., Samaj, J., Palme, K., Robinson, D. G., Matoh, T., McCurdy, D. W., Menzel, D., and Volkmann, D. (2002). F-actin-dependent endocytosis of cell wall pectins in meristematic root cells. Insights from brefeldin A-induced compartments. Plant Physiol. 130, 422-431. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basu, D., El-Assal Sel, D., Le, J., Mallery, E. L., and Szymanski, D. B. (2004). Interchangeable functions of Arabidopsis PIROGI and the human WAVE complex subunit SRA1 during leaf epidermal development. Development 131, 4345-4355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

