Licensing for DNA replication requires a strict sequential assembly of Cdc6 and Cdt1 onto chromatin in Xenopus egg extracts
- PMID: 15687385
- PMCID: PMC548366
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki226
Licensing for DNA replication requires a strict sequential assembly of Cdc6 and Cdt1 onto chromatin in Xenopus egg extracts
Abstract
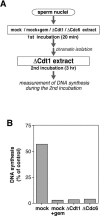
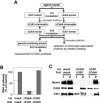
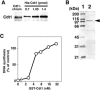
Replication origins are licensed for a single initiation event by the loading of Mcm2-7 proteins during late mitosis and G1. Sequential associations of origin recognition complex, Cdc6 and Mcm2-7 are essential for completion of the licensing. Although Cdt1 also binds to the chromatin when the licensing reaction takes place, whether the binding is a requirement for Cdt1 to function is unclear. To analyze the relevance of the chromatin association of Cdt1, we carried out chromatin transfer experiments using either immunodepleted Xenopus egg extracts or purified proteins. Licensing assay and immunoblotting analyses indicated that Cdt1 could only license DNA replication and load Mcm2-7 onto DNA when it binds to chromatin that has already associated with Cdc6. These results provide evidence supporting that Cdc6 and Cdt1 must bind to chromatin in a strict order for DNA licensing to occur.
Figures

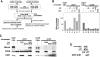
Similar articles
-
Recruitment of Xenopus Scc2 and cohesin to chromatin requires the pre-replication complex.Nat Cell Biol. 2004 Oct;6(10):991-6. doi: 10.1038/ncb1177. Epub 2004 Sep 26. Nat Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15448702
-
A Cdt1-geminin complex licenses chromatin for DNA replication and prevents rereplication during S phase in Xenopus.EMBO J. 2006 Dec 13;25(24):5764-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601436. Epub 2006 Nov 23. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 17124498 Free PMC article.
-
MCM interference during licensing of DNA replication in Xenopus egg extracts-Possible Role of a C-terminal region of MCM3.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(4):492-505. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1415681. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 29261034 Free PMC article.
-
Control of DNA replication licensing in a cell cycle.Genes Cells. 2002 Jun;7(6):523-34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2002.00544.x. Genes Cells. 2002. PMID: 12059957 Review.
-
Getting a grip on licensing: mechanism of stable Mcm2-7 loading onto replication origins.Mol Cell. 2006 Jan 20;21(2):143-4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.01.003. Mol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16427002 Review.
Cited by
-
Preventing re-replication of chromosomal DNA.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jun;6(6):476-86. doi: 10.1038/nrm1663. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15928711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The minichromosome maintenance proteins 2-7 (MCM2-7) are necessary for RNA polymerase II (Pol II)-mediated transcription.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 15;284(20):13466-13472. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809471200. Epub 2009 Mar 23. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19318354 Free PMC article.
-
Tsetse fly (Glossina pallidipes) midgut responses to Trypanosoma brucei challenge.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Dec 19;10(1):614. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2569-7. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 29258576 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirement of DNA replication factors for subtelomeric ARS consensus sequence protosilencers in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2006 Dec;174(4):1801-10. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.063446. Epub 2006 Sep 15. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16980387 Free PMC article.
-
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Noc3 is essential for ribosome biogenesis and cell division but not DNA replication.Eukaryot Cell. 2008 Sep;7(9):1433-40. doi: 10.1128/EC.00119-08. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Eukaryot Cell. 2008. PMID: 18606828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell S.P., Dutta A. DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002;71:333–374. - PubMed
-
- Nishitani H., Lygerou Z. Control of DNA replication licensing in a cell cycle. Genes Cells. 2002;7:523–534. - PubMed
-
- Diffley J.F., Labib K. The chromosome replication cycle. J. Cell. Sci. 2002;115:869–872. - PubMed
-
- Maiorano D., Moreau J., Mechali M. XCDT1 is required for the assembly of pre-replicative complexes in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 2000;404:622–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

