Cytogenetic abnormalities and fragile-X syndrome in Autism Spectrum Disorder
- PMID: 15655077
- PMCID: PMC548305
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-6-3
Cytogenetic abnormalities and fragile-X syndrome in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
Background: Autism is a behavioral disorder with impaired social interaction, communication, and repetitive and stereotypic behaviors. About 5-10 % of individuals with autism have 'secondary' autism in which an environmental agent, chromosome abnormality, or single gene disorder can be identified. Ninety percent have idiopathic autism and a major gene has not yet been identified. We have assessed the incidence of chromosome abnormalities and Fragile X syndrome in a population of autistic patients referred to our laboratory.
Methods: Data was analyzed from 433 patients with autistic traits tested using chromosome analysis and/or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and/or molecular testing for fragile X syndrome by Southern and PCR methods.
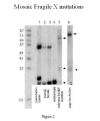
Results: The median age was 4 years. Sex ratio was 4.5 males to 1 female [354:79]. A chromosome (cs) abnormality was found in 14/421 [3.33 %] cases. The aberrations were: 4/14 [28%] supernumerary markers; 4/14 [28%] deletions; 1/14 [7%] duplication; 3/14 [21%] inversions; 2/14 [14%] translocations. FISH was performed on 23 cases for reasons other than to characterize a previously identified cytogenetic abnormality. All 23 cases were negative. Fragile-X testing by Southern blots and PCR analysis found 7/316 [2.2 %] with an abnormal result. The mutations detected were: a full mutation (fM) and abnormal methylation in 3 [43 %], mosaic mutations with partial methylation of variable clinical significance in 3 [43%] and a permutation carrier [14%]. The frequency of chromosome and fragile-X abnormalities appears to be within the range in reported surveys (cs 4.8-1.7%, FRAX 2-4%). Limitations of our retrospective study include paucity of behavioral diagnostic information, and a specific clinical criterion for testing.
Conclusions: Twenty-eight percent of chromosome abnormalities detected in our study were subtle; therefore a high resolution cytogenetic study with a scrutiny of 15q11.2q13, 2q37 and Xp23.3 region should be standard practice when the indication is autism. The higher incidence of mosaic fragile-X mutations with partial methylation compared to FRAXA positive population [50% vs 15-40%] suggests that faint bands and variations in the Southern band pattern may occur in autistic patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular and cytogenetic investigations of the fragile X region including the Frax A and Frax E CGG trinucleotide repeat sequences in families multiplex for autism and related phenotypes.Hum Hered. 1997 Sep-Oct;47(5):254-62. doi: 10.1159/000154421. Hum Hered. 1997. PMID: 9358013
-
Molecular genetic analysis of the FMR-1 gene in a large collection of autistic patients.Hum Genet. 1997 Aug;100(2):224-9. doi: 10.1007/s004390050495. Hum Genet. 1997. PMID: 9254854
-
The genetics of autism.Pediatrics. 2004 May;113(5):e472-86. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.5.e472. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15121991 Review.
-
The fragile X marker and autism in perspective.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1989 May;28(3):417-21. doi: 10.1097/00004583-198905000-00019. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1989. PMID: 2738009
-
A case with a ring chromosome 13 in a cohort of 203 children with non-syndromic autism and review of the cytogenetic literature.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2014;144(1):1-8. doi: 10.1159/000365909. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 25171325 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic yield of array CGH in patients with autism spectrum disorder in Hong Kong.Clin Transl Med. 2016 Dec;5(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s40169-016-0098-1. Epub 2016 May 16. Clin Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27271878 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Autism with Ring Chromosome 14.Iran J Public Health. 2013 Nov;42(11):1316-20. Iran J Public Health. 2013. PMID: 26171345 Free PMC article.
-
Deep exon resequencing of DLGAP2 as a candidate gene of autism spectrum disorders.Mol Autism. 2013 Aug 1;4(1):26. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-4-26. Mol Autism. 2013. PMID: 23915500 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Sequencing in Autism Spectrum Disorder.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019 Aug 1;9(8):a026872. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026872. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019. PMID: 30420340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of autism and mental retardation: A spoonful from the sea!Indian J Hum Genet. 2009 Sep;15(3):85-7. doi: 10.4103/0971-6866.60181. Indian J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 21088710 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Prevalence of Autism in Brick Township, New Jersey, 1998. Atlanta, Ga: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Community Report. 2000. http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/dd/rpttoc.htm
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

