Natural killer cells utilize both perforin and gamma interferon to regulate murine cytomegalovirus infection in the spleen and liver
- PMID: 15596864
- PMCID: PMC538682
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.661-667.2005
Natural killer cells utilize both perforin and gamma interferon to regulate murine cytomegalovirus infection in the spleen and liver
Abstract
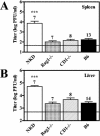
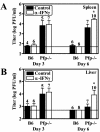
Natural killer (NK) cells are critical for innate regulation of the acute phase of murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection and have been reported to utilize perforin (Pfp)- and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-dependent effector mechanisms in an organ-specific manner to regulate MCMV infection in the spleen and liver. In this study, we further examined the roles of NK cells, Pfp, and IFN-gamma in innate immunity to MCMV infection. With the recently described NK cell-deficient (NKD) mouse, we confirmed previous findings that NK cells, but not NKT cells, are required for control of the acute phase of MCMV infection in spleen and liver cells. Interestingly, we found that Pfp and IFN-gamma are each important for regulating MCMV replication in both the spleen and the liver. Moreover, NK cells can regulate MCMV infection in the spleens and livers of Pfp(-/-) mice in a Pfp-independent manner and can use an IFN-gamma-independent mechanism to control MCMV infection in IFN-gamma(-/-) mice. Thus, contrary to previous reports, NK cells utilize both Pfp and IFN-gamma to control MCMV infection in the spleen and liver.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Immunoregulatory cytokine networks: 60 years of learning from murine cytomegalovirus.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Jun;204(3):345-54. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0412-3. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25850988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct organ-dependent mechanisms for the control of murine cytomegalovirus infection by natural killer cells.J Virol. 1997 Jan;71(1):267-75. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.1.267-275.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 8985346 Free PMC article.
-
The role of LY49 NK cell subsets in the regulation of murine cytomegalovirus infections.J Immunol. 1999 Jan 15;162(2):718-26. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 9916691
-
The roles of interferon-gamma and perforin in antiviral immunity in mice that differ in genetically determined NK-cell-mediated antiviral activity.Immunol Cell Biol. 2009 Oct;87(7):559-66. doi: 10.1038/icb.2009.41. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Immunol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19564888
-
Calling in the troops: regulation of inflammatory cell trafficking through innate cytokine/chemokine networks.Viral Immunol. 2003;16(3):291-306. doi: 10.1089/088282403322396109. Viral Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14583145 Review.
Cited by
-
Ly49h-deficient C57BL/6 mice: a new mouse cytomegalovirus-susceptible model remains resistant to unrelated pathogens controlled by the NK gene complex.J Immunol. 2008 Nov 1;181(9):6394-405. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.9.6394. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18941230 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of macrophage activation syndrome and treatment progression.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 26;15:1389710. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1389710. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38736876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoregulatory cytokine networks: 60 years of learning from murine cytomegalovirus.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Jun;204(3):345-54. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0412-3. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25850988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-15-PI3K-AKT-mTOR: A Critical Pathway in the Life Journey of Natural Killer Cells.Front Immunol. 2015 Jul 20;6:355. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00355. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26257729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic regulation of NK cell antiviral functions during cytomegalovirus infection.J Leukoc Biol. 2023 May 2;113(5):525-534. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiad018. J Leukoc Biol. 2023. PMID: 36843434 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson, K. P., Y. S. Lie, M. A. Low, and E. H. Fennie. 1993. Effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment on mortality in murine cytomegalovirus-infected mice. Antiviral Res. 21:343-355. - PubMed
-
- Arase, H., E. S. Mocarski, A. E. Campbell, A. B. Hill, and L. L. Lanier. 2002. Direct recognition of cytomegalovirus by activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors. Science 296:1323-1326. - PubMed
-
- Baetz, K., S. Isaaz, and G. M. Griffiths. 1995. Loss of cytotoxic T lymphocyte function in Chediak-Higashi syndrome arises from a secretory defect that prevents lytic granule exocytosis. J. Immunol. 154:6122-6131. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft, G. J., G. R. Shellam, and J. E. Chalmer. 1981. Genetic influences on the augmentation of natural killer (NK) cells during murine cytomegalovirus infection: correlation with patterns of resistance. J. Immunol. 126:988-994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

