Activation of Arp2/3 complex-dependent actin polymerization by plant proteins distantly related to Scar/WAVE
- PMID: 15534215
- PMCID: PMC528980
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407392101
Activation of Arp2/3 complex-dependent actin polymerization by plant proteins distantly related to Scar/WAVE
Abstract
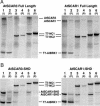
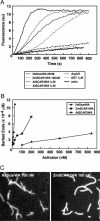
The Arp2/3 complex, a highly conserved nucleator of F-actin polymerization, plays a key role in the regulation of actin dynamics eukaryotic cells. In animal cells and yeasts, Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome protein (WASP)/suppressor of cAMP receptor (Scar)/WASP family verprolin homologous (WAVE) family proteins activate the Arp2/3 complex in response to localized cues. Like other eukaryotes, plants have an Arp2/3 complex, which has recently been shown to play an important role in F-actin organization and cell morphogenesis. However, no activators of the Arp2/3 complex have been identified in plants, which lack obvious homologs of WASP/Scar/WAVE family proteins. Here, we identify a family of Scar/WAVE-related plant Arp2/3 activators. Like Scar/WAVE proteins, four proteins identified in Arabidopsis thaliana (AtSCAR1 to AtSCAR4) and one in maize (ZmSCAR1) have a C-terminal WASP homology 2 (WH2)/acidic (WA)-verprolin homology/cofilin homology/acidic (VCA)-like domain, which we show can activate the bovine Arp2/3 complex. At their N termini, AtSCAR1 to ATSCAR4, along with a fifth protein lacking a VCA/WA-like domain at its C terminus (At4g18600), are related to the N-terminal Scar homology domains of Scar/WAVE family proteins. Analysis of gene expression patterns suggests functional redundancy among members of the AtSCAR family. Full-length AtSCAR1 and ATSCAR3 proteins and their Scar homology domains bind in vitro to AtBRICK 1 (AtBRK1), the Arabidopsis homolog of HSPC300, a WAVE-binding protein recently identified as a component of a complex implicated in the regulation of Scar/WAVE activity. Thus, AtSCAR proteins are likely to function in association with AtBRK1, and perhaps other Arabidopsis homologs of WAVE complex components, to regulate activation of the Arp2,3 complex in vivo.
Figures

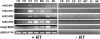
Similar articles
-
BRICK1/HSPC300 functions with SCAR and the ARP2/3 complex to regulate epidermal cell shape in Arabidopsis.Development. 2006 Mar;133(6):1091-100. doi: 10.1242/dev.02280. Epub 2006 Feb 15. Development. 2006. PMID: 16481352
-
NAPP and PIRP encode subunits of a putative wave regulatory protein complex involved in plant cell morphogenesis.Plant Cell. 2004 Sep;16(9):2335-49. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.023739. Epub 2004 Aug 17. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15316111 Free PMC article.
-
SCAR is a primary regulator of Arp2/3-dependent morphological events in Drosophila.J Cell Biol. 2002 Feb 18;156(4):689-701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200109057. Epub 2002 Feb 18. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11854309 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of actin filament network formation through ARP2/3 complex: activation by a diverse array of proteins.Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:649-76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.70.1.649. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11395419 Review.
-
Spatial and temporal regulation of actin polymerization for cytoskeleton formation through Arp2/3 complex and WASP/WAVE proteins.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2002 Mar;51(3):113-22. doi: 10.1002/cm.10020. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2002. PMID: 11921168 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Formins control dynamics of F-actin in the central cell of Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Signal Behav. 2021 Aug 3;16(8):1920192. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2021.1920192. Epub 2021 May 4. Plant Signal Behav. 2021. PMID: 33944667 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the molecular evolution of fertilization mechanism in land plants.Plant Reprod. 2021 Dec;34(4):353-364. doi: 10.1007/s00497-021-00414-3. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Plant Reprod. 2021. PMID: 34061252 Review.
-
Rice TUTOU1 Encodes a Suppressor of cAMP Receptor-Like Protein That Is Important for Actin Organization and Panicle Development.Plant Physiol. 2015 Oct;169(2):1179-91. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00229. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26243616 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Modulation of Root Cell Wall Architecture Confers Resistance to an Oomycete Pathogen.Curr Biol. 2020 Nov 2;30(21):4165-4176.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.08.011. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32888486 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms controlling pavement cell shape in Arabidopsis leaves.Plant Cell Rep. 2009 Aug;28(8):1147-57. doi: 10.1007/s00299-009-0729-8. Epub 2009 Jun 16. Plant Cell Rep. 2009. PMID: 19529941 Review.
References
-
- Pollard, T. D. & Borisy, G. G. (2003) Cell 112, 453-465. - PubMed
-
- Weaver, A. M., Young, M. E., Lee, W. L. & Cooper, J. A. (2003) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 23-30. - PubMed
-
- Welch, M. D. & Mullins, R. D. (2002) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 18, 247-288. - PubMed
-
- Klahre, U. & Chua, N. H. (1999) Plant Mol. Biol. 41, 65-73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

