Tyrosine dephosphorylation of STAT3 in SARS coronavirus-infected Vero E6 cells
- PMID: 15527783
- PMCID: PMC7125663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.10.005
Tyrosine dephosphorylation of STAT3 in SARS coronavirus-infected Vero E6 cells
Abstract
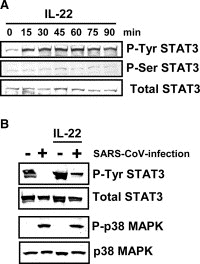
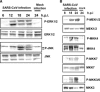
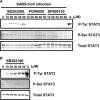
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) has become a global public health emergency. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and its downstream targets are activated in SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV)-infected Vero E6 cells and activation of p38 MAPK enhances the cytopathic effects of SARS-CoV infection. In addition, weak activation of Akt cannot prevent SARS-CoV infection-induced apoptosis in Vero E6 cells. In the present study, we demonstrated that signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3, which is constitutively phosphorylated at tyrosine (Tyr)-705 and slightly phosphorylated at serine (Ser)-727 in Vero E6 cells, was dephosphorylated at Tyr-705 on SARS-CoV infection. In addition to phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in virus-infected cells, other MAPKs, i.e., extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), were phosphorylated. Although inhibitors of ERK1/2 and JNK (PD98059 and SP600125) had no effect on phosphorylation status of STAT3, inhibitors of p38 MAPK (SB203580 and SB202190) partially inhibited dephosphorylation of STAT3 at Tyr-705. Tyr-705-phosphorylated STAT3 was localized mainly in the nucleus in mock infected cells, whereas STAT3 disappeared from the nucleus in virus-infected cells. As STAT3 acts as an activator of transcription in the nucleus, these results suggest that STAT3 lacks its activity on transcription in SARS-CoV-infected Vero E6 cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
JNK and PI3k/Akt signaling pathways are required for establishing persistent SARS-CoV infection in Vero E6 cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Jun 30;1741(1-2):4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2005.04.004. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 15916886 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of p90RSK phosphorylation by SARS-CoV infection in Vero E6 cells.FEBS Lett. 2006 Feb 20;580(5):1417-24. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.066. Epub 2006 Jan 30. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16458888 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of cell proliferation by SARS-CoV infection in Vero E6 cells.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2006 Mar;46(2):236-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2005.00028.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16487305 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction in SARS-CoV-infected cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Apr;1102(1):86-95. doi: 10.1196/annals.1408.006. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17470913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 cytopathic effect (host tox counterscreen).SARS-CoV-2 Assays [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS); 2020–. SARS-CoV-2 Assays [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS); 2020–. PMID: 35512049 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of protein expression changes of the Vero E6 cells infected with classic PEDV strain CV777 by using quantitative proteomic technique.J Virol Methods. 2015 Jun 15;218:27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.03.002. Epub 2015 Mar 14. J Virol Methods. 2015. PMID: 25783682 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of cytotoxicity against Vero E6 cells persistently infected with SARS-CoV by Mycoplasma fermentans.Arch Virol. 2007;152(5):1019-25. doi: 10.1007/s00705-006-0924-7. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Arch Virol. 2007. PMID: 17277901 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine regulation in SARS coronavirus infection compared to other respiratory virus infections.J Med Virol. 2006 Apr;78(4):417-24. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20556. J Med Virol. 2006. PMID: 16482545 Free PMC article.
-
The Staphylococcus aureus protein IsdA increases SARS CoV-2 replication by modulating JAK-STAT signaling.iScience. 2023 Feb 17;26(2):105975. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.105975. Epub 2023 Jan 13. iScience. 2023. PMID: 36687318 Free PMC article.
-
A pathway map of signaling events triggered upon SARS-CoV infection.J Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Dec;15(4):595-600. doi: 10.1007/s12079-021-00642-2. Epub 2021 Sep 6. J Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34487344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rota P.A., Oberste M.S., Monroe S.S., Nix W.A., Campagnoli R., Icenogle J.P., Penaranda S., Bankamp B., Maher K., Chen M.H., Tong S., Tamin A., Lowe L., Frace M., DeRisi J.L., Chen Q., Wang D., Erdman D.D., Peret T.C., Burns C., Ksiazek T.G., Rollin P.E., Sanchez A., Liffick S., Holloway B., Limor J., McCaustland K., Olsen-Rasmussen M., Fouchier R., Gunther S., Osterhaus A.D., Drosten C., Pallansch M.A., Anderson L.J., Bellini W.J., Science, 300, (2003), 1394– 1399. - PubMed
-
- Marra M.A., Jones S.J., Astell C.R., Holt R.A., Brooks-Wilson A., Butterfield Y.S., Khattra J., Asano J.K., Barber S.A., Chan S.Y., Cloutier A., Coughlin S.M., Freeman D., Girn N., Griffith O.L., Leach S.R., Mayo M., McDonald H., Montgomery S.B., Pandoh P.K., Petrescu A.S., Robertson A.G., Schein J.E., Siddiqui A., Smailus D.E., Stott J.M., Yang G.S., Plummer F., Andonov A., Artsob H., Bastien N., Bernard K., Booth T.F., Bowness D., Czub M., Drebot M., Fernando L., Flick R., Garbutt M., Gray M., Grolla A., Jones S., Feldmann H., Meyers A., Kabani A., Li Y., Normand S., Stroher U., Tipples G.A., Tyler S., Vogrig R., Ward D., Watson B., Brunham R.C., Krajden M., Petric M., Skowronski D.M., Upton C., Roper R.L., Science, 300, (2003), 1399– 1404. - PubMed
-
- Garrington T.P., Johnson G.L., Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol, 11, (1999), 211– 218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

